While studies have focused on early readmissions or readmissions during the same hospitalization in a pediatric intensive care unit, little is known about the children with recurrent admissions. We sought to assess the characteristics of patients readmitted within 1 year in a Brazilian pediatric intensive care unit.
MethodsThis was a retrospective study carried out in a tertiary pediatric intensive care unit. The outcome was the maximum number of readmissions experienced by each child within any 365-day interval during a 5-year follow-up period.
ResultsOf the 758 total eligible admissions, 75 patients (9.8%) were readmissions. Those patients accounted for 33% of all pediatric intensive care unit bed care days. Median time to readmission was 73 days for all readmissions. Logistic regression showed that complex chronic conditions (odds ratio 1.07), severe to moderate cognitive disability (odds ratio 1.08), and use of technology assistance (odds ratio 1.17) were associated with readmissions. Multiple admissions had a significantly prolonged duration of mechanical ventilation (8 vs. 6 days), longer length of pediatric intensive care unit (7 vs 4 days) and hospital stays (20 vs 9 days), and higher mortality rate (21.3% vs 5.1%) compared with index admissions.
ConclusionThe rate of pediatric intensive care unit readmissions within 1 year was low; however, it was associated with a relevant number of bed care days and worse outcomes. A 30-day index of readmission may be inadequate to mirror the burden of pediatric intensive care unit readmissions. Patients with complex chronic conditions, poor functional status or technology assistance are at higher risk for readmissions. Future studies should address the impact of qualitative interventions on healthcare and recurrent admissions.
Apesar dos estudos terem focado em reinternações precoces ou reinternações durante a mesma internação na unidade de terapia intensiva pediátrica, pouco se sabe sobre essas crianças com internações recorrentes. Buscamos avaliar as características dos pacientes reinternados em 1 ano em uma unidade de terapia intensiva pediátrica brasileira.
MétodosEste foi um estudo retrospectivo realizado em uma unidade de terapia intensiva pediátrica terciária. O resultado foi o número máximo de reinternações por cada criança em qualquer período de 365 dias durante um período de acompanhamento de 5 anos.
ResultadosDo total de 758 internações elegíveis, 75 pacientes (9,8%) foram de reinternações. Esses pacientes representaram 33% de todos os dias de cuidados com os internados na unidade de terapia intensiva pediátrica. O tempo mediano para a reinternação foi 73 dias para todas as reinternações. A regressão logística mostrou que as doenças crônicas complexas (razão de chance de 1,07), deficiência cognitiva grave a moderada (razão de chance de 1,08) e uso de suporte de aparelhos tecnológicos (razão de chance de 1,17) foram associados às reinternações. As múltiplas internações apresentaram duração significativamente prolongada na ventilação mecânica (8 em comparação a 6 dias), maior tempo de internação na unidade de terapia intensiva pediátrica (7 em comparação a 4 dias) e tempos de internação (20 em comparação a 9 dias) e maior taxa de mortalidade (21,3% em comparação a 5,1%), em comparação às internações iniciais.
ConclusãoA taxa de reinternações na unidade de terapia intensiva pediátrica em 1 ano foi baixa, porém foi associada a um número relevante de cuidados durante internação e piores resultados. Um índice de reinternação de 30 dias pode ser inadequado para refletir a grande número de reinternações na unidade de terapia intensiva pediátrica. Os pacientes com doenças crônicas complexas, estado funcional ruim ou suporte de aparelhos tecnológicos correm maior risco de reinternações. Estudos futuros devem abordar o impacto das intervenções qualitativas sobre os serviços de saúde e as internações recorrentes.
A few pediatric studies show that 1.2–31%1–7 of children discharged from pediatric intensive care units (PICU) in developed countries will be readmitted at any time. Some national reporting agencies such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid and the National Quality Forum8 are using readmissions as a standard measure of quality. Prior studies of readmissions among children focus mainly on an index admission and an early subsequent readmission experience, often within 30 days.4–6,9 However, this approach may underestimate the impact of patients experiencing recurrent readmissions during the weeks and months after discharge.10
Although repeated readmissions may be an obstacle to PICU efficiency and potentially jeopardize medical and surgical admissions, the current knowledge about the epidemiology of readmissions in PICUs in the long term is restricted to one single study involving North American PICUs.7
Studies examining risks and determinants of rehospitalization among children suggest that some repeated admissions can be amenable to a high-quality outpatient care, while others may be avoidable by effective discharge guidance and appropriate clinical pathways.11 Knowing more about the factors that may weight on PICU readmission rates can help to better contend with this ongoing challenge. Yet, it is important for the healthcare system to identify the children who make the most intensive and repeated use of PICU resources.
Therefore, the objectives of this study were to assess the rate of readmissions within 1 year in a Brazilian PICU and to compare the characteristics of single admissions vs one or multiple readmissions in the PICU. Secondarily, we sought the potential risk factors for PICU readmissions.
MethodsStudy design and settingThis non-concurrent, prospective cohort study was conducted in an eight-bed medical-surgical PICU of a public, regional care hospital. The PICU is not designed to handle specialist congenital heart surgery or burn cases, and bone marrow and solid organ transplants are not performed in the hospital. Our population is predominantly composed by children with medical conditions, although patients undergoing planned or emergency surgical, thoracosurgical and neurosurgical procedures are also admitted at the PICU. The local institutional review board approved the study and waived the need for informed consent from the children's parents (approval number 1266926/CAAE 49586415200005442).
The study population included all consecutive patients aged between 1 month and 16 years admitted at our PICU. As of 2012, each patient admitted to the PICU was followed for one year in order to identify new hospitalizations (of the same patient) in the PICU (readmissions). Patients were excluded if they (1) died during their first admission; (2) were transferred to another hospital or to our long-term mechanical ventilation unit (separate intermediate unit); or (3) had a planned readmission.
Data collectionThe data were prospectively collected from patient's records during the PICU admission and inputted into an Excel database (Microsoft Excel, 2011), from where they were retrieved for analysis. This electronic database is part of an electronic database designed to monitor quality indicators at our PICU.
The demographic and clinical variables collected included age, gender, weight, PICU admission diagnosis (as determined by the clinical care team), presence of a chronic condition, baseline Pediatric Cerebral Performance Category,12 location before PICU admission, need for invasive support (mechanical ventilation and renal replacement therapy), vasopressors and blood transfusion, multidrug-resistant bacteria infection during PICU stay, and the severity of illness at PICU admission as measured by the Pediatric Risk of Mortality (PRISM) II13 and Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction score.14 We also collected duration of mechanical ventilation and PICU as well as length of hospital stays.
DefinitionsReadmission was defined as new admission to PICU of a patient who had been previously admitted to PICU (index PICU admission) within a 365-day interval following the index PICU admission, considering PICU discharge as time zero. Readmission could have occurred in the same hospitalization or in a different one. The number of readmissions was defined as the total number of PICU readmissions, following an index admission, experienced by each patient within a 365-day interval within the follow-up period study.
We used Feudtner's definition of complex chronic conditions (CCCs)15 as well as a modified list of chronic conditions developed elsewhere.16 In addition, patients were considered with technology assistance if they had a medical technology used to maintain their health status, such as gastrostomy, tracheostomy, cerebrospinal fluid ventricular shunt, permanent indwelling catheter, and pacemaker.17
The possible sources of the PICU admission were the emergency department, operating room/emergency post-operative status, operating room/elective post-operative status, transfer from other institutions, or in-hospital ward transfer. Also, a multidrug-resistant pathogenic bacteria was defined based on a standard definition.18
Study outcomesThe primary outcome variable for the analysis was PICU readmission within 1 year of an index discharge from the PICU, during the same, or in a different, hospitalization. We subsequently assessed the rate of PICU readmission and its risk factors by comparing patients with and without readmission.
Statistical analysisDescriptive statistics were performed for all variables. The results are expressed as numerical values and percentages for categorical variables, and as medians and quartiles (25th–75th percentile) for continuous variables. The median difference and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated when appropriate. Normality was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Comparisons between readmitted and non-readmitted patients to the PICU were based on the Mann–Whitney U test for continuous variables and the chi-squared test for categorical variables, or Fisher's exact test if one expected that the cell value would be less than 5 (categorical variables). The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was performed with readmission as the dependent variable in order to identify factors associated with PICU readmissions. All variables in the univariate analysis with a p value lower than 0.05 were included as independent variables, as well as additional variables considered of clinical relevance that were chosen a priori such as the severity of illness score. All statistical tests were two-tailed, and a p value lower than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. The data were analyzed using the Statistical Program for Social Sciences software version 16.0 (IBM SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) and R software (version 3.5).
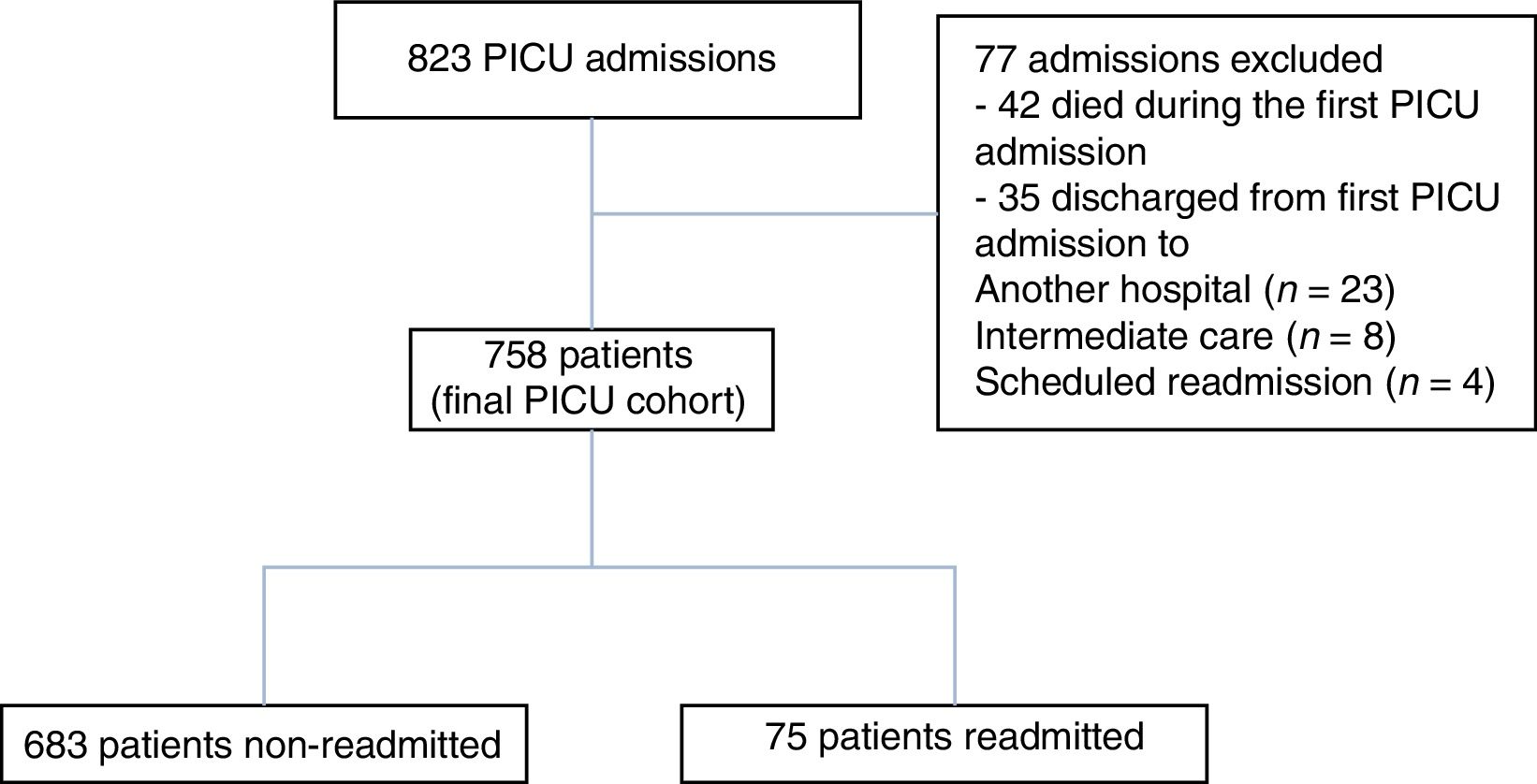
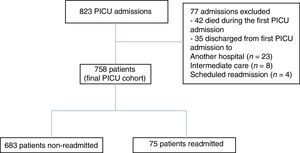
ResultsPatient characteristicsFrom January 2012 to December 2016, a total of 835 patients were admitted to PICU (Fig. 1). After excluding 77 patients, 758 children experiencing a total of 867 admissions were included for analysis. Among them, 75 patients (9.8%) experienced 109 readmissions within 365 days of a prior admission; 58 had one readmission, 5 had two readmissions, 8 had three readmissions and 4 had four or more readmissions. Thus, 2.5% of our total population needed two or more PICU readmissions within 1-year. Out of the readmitted patients, 38 (50.6%) were readmitted to PICU during the same hospitalization. Limiting the analysis to the first PICU readmission, the median interval between primary discharge and readmission was 73 days (IQR, 28–129). While the median interval was 28.5 days (IQR, 13.5–65.5) for readmission in the same hospitalization, the median interval was 117 days (IQR, 81.5–208) for those patients readmitted in different hospitalizations. Only two patients were readmitted early (i.e. ≤72h). Of the 75 patients readmitted, 42 (56%) were readmitted as a result of a new condition, whereas 33 (44%) were readmitted due to worsening of their preexisting conditions (p=0.139). Readmissions accounted for 33% (2648 days) of all PICU bed care days (8022 days).
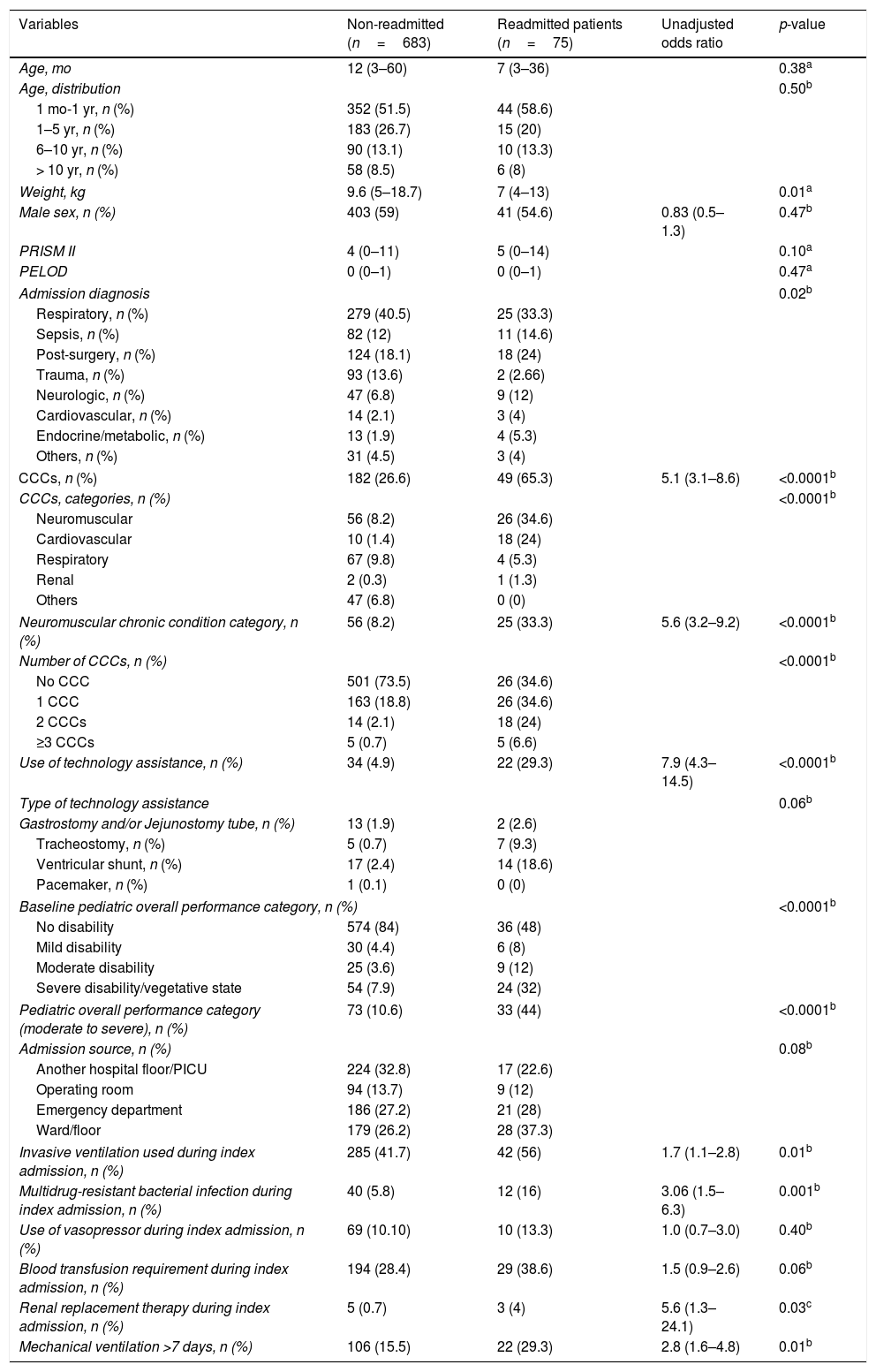
The patient characteristics are presented in Table 1. Admission diagnosis at index PICU entry was statistically different between non-readmitted and readmitted patients. There was no difference between the groups for admissions due to respiratory disease, sepsis, postoperative care, and trauma, whereas other conditions were more prevalent in the readmitted subgroup (p=0.023). As shown in Table 1, readmitted patients had significantly lower median of weight, increased moderate/severe disability, higher rate of multidrug resistant infection during index admission, and more presence of CCCs. Patients experiencing readmission had significantly more neuromuscular conditions such as CCC than non-readmitted patients.
Characteristics of PICU patients and their index admissions by readmission status.
| Variables | Non-readmitted (n=683) | Readmitted patients (n=75) | Unadjusted odds ratio | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mo | 12 (3–60) | 7 (3–36) | 0.38a | |
| Age, distribution | 0.50b | |||
| 1 mo-1 yr, n (%) | 352 (51.5) | 44 (58.6) | ||
| 1–5 yr, n (%) | 183 (26.7) | 15 (20) | ||
| 6–10 yr, n (%) | 90 (13.1) | 10 (13.3) | ||
| > 10 yr, n (%) | 58 (8.5) | 6 (8) | ||
| Weight, kg | 9.6 (5–18.7) | 7 (4–13) | 0.01a | |
| Male sex, n (%) | 403 (59) | 41 (54.6) | 0.83 (0.5–1.3) | 0.47b |
| PRISM II | 4 (0–11) | 5 (0–14) | 0.10a | |
| PELOD | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–1) | 0.47a | |
| Admission diagnosis | 0.02b | |||
| Respiratory, n (%) | 279 (40.5) | 25 (33.3) | ||
| Sepsis, n (%) | 82 (12) | 11 (14.6) | ||
| Post-surgery, n (%) | 124 (18.1) | 18 (24) | ||
| Trauma, n (%) | 93 (13.6) | 2 (2.66) | ||
| Neurologic, n (%) | 47 (6.8) | 9 (12) | ||
| Cardiovascular, n (%) | 14 (2.1) | 3 (4) | ||
| Endocrine/metabolic, n (%) | 13 (1.9) | 4 (5.3) | ||
| Others, n (%) | 31 (4.5) | 3 (4) | ||
| CCCs, n (%) | 182 (26.6) | 49 (65.3) | 5.1 (3.1–8.6) | <0.0001b |
| CCCs, categories, n (%) | <0.0001b | |||
| Neuromuscular | 56 (8.2) | 26 (34.6) | ||
| Cardiovascular | 10 (1.4) | 18 (24) | ||
| Respiratory | 67 (9.8) | 4 (5.3) | ||
| Renal | 2 (0.3) | 1 (1.3) | ||
| Others | 47 (6.8) | 0 (0) | ||
| Neuromuscular chronic condition category, n (%) | 56 (8.2) | 25 (33.3) | 5.6 (3.2–9.2) | <0.0001b |
| Number of CCCs, n (%) | <0.0001b | |||
| No CCC | 501 (73.5) | 26 (34.6) | ||
| 1 CCC | 163 (18.8) | 26 (34.6) | ||
| 2 CCCs | 14 (2.1) | 18 (24) | ||
| ≥3 CCCs | 5 (0.7) | 5 (6.6) | ||
| Use of technology assistance, n (%) | 34 (4.9) | 22 (29.3) | 7.9 (4.3–14.5) | <0.0001b |
| Type of technology assistance | 0.06b | |||
| Gastrostomy and/or Jejunostomy tube, n (%) | 13 (1.9) | 2 (2.6) | ||
| Tracheostomy, n (%) | 5 (0.7) | 7 (9.3) | ||
| Ventricular shunt, n (%) | 17 (2.4) | 14 (18.6) | ||
| Pacemaker, n (%) | 1 (0.1) | 0 (0) | ||
| Baseline pediatric overall performance category, n (%) | <0.0001b | |||
| No disability | 574 (84) | 36 (48) | ||
| Mild disability | 30 (4.4) | 6 (8) | ||
| Moderate disability | 25 (3.6) | 9 (12) | ||
| Severe disability/vegetative state | 54 (7.9) | 24 (32) | ||
| Pediatric overall performance category (moderate to severe), n (%) | 73 (10.6) | 33 (44) | <0.0001b | |
| Admission source, n (%) | 0.08b | |||
| Another hospital floor/PICU | 224 (32.8) | 17 (22.6) | ||
| Operating room | 94 (13.7) | 9 (12) | ||
| Emergency department | 186 (27.2) | 21 (28) | ||
| Ward/floor | 179 (26.2) | 28 (37.3) | ||
| Invasive ventilation used during index admission, n (%) | 285 (41.7) | 42 (56) | 1.7 (1.1–2.8) | 0.01b |
| Multidrug-resistant bacterial infection during index admission, n (%) | 40 (5.8) | 12 (16) | 3.06 (1.5–6.3) | 0.001b |
| Use of vasopressor during index admission, n (%) | 69 (10.10) | 10 (13.3) | 1.0 (0.7–3.0) | 0.40b |
| Blood transfusion requirement during index admission, n (%) | 194 (28.4) | 29 (38.6) | 1.5 (0.9–2.6) | 0.06b |
| Renal replacement therapy during index admission, n (%) | 5 (0.7) | 3 (4) | 5.6 (1.3–24.1) | 0.03c |
| Mechanical ventilation >7 days, n (%) | 106 (15.5) | 22 (29.3) | 2.8 (1.6–4.8) | 0.01b |
Data are expressed as median (percentile 25, percentile 75) or number (%).
CI, confidence interval; CCC, complex chronic condition; PRISM, Pediatric Risk of Mortality; PELOD, Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction; PICU, pediatric intensive care unit.
Respiratory failure (n=25, 33%), cerebrospinal shunt-failure/infection (n=14, 18.6%), sepsis (n=11, 14.6%), and seizure (n=6, 8%) were the most prevalent reasons for readmissions.
Overall, 66 patients (8.7%) had technology assistance. Of these, 50 (75.7%) were patients with CCCs. Also, technology assistance was significantly higher for patients experiencing multiple admissions compared with those who had a single admission (29.3% vs 4.9%, p≤0.0001).
The most prevalent technologies among readmitted patients were cerebrospinal ventricular shunt (n=14), tracheostomy (n=7), and gastrostomy tube (n=2).
Predictors of PICU readmissionThe LASSO regression was conducted to identify the risk factors for PICU readmissions. PICU readmission was associated with presence of CCC (odds ratio 1.07, 95% CI: 1.09–1.13), severe to moderate cognitive disability (odds ratio 1.08, 95% CI: 1.05–1.29), and use of technology assistance (odds ratio 1.17, 95% CI: 1–1.17) after controlling the model for severity of illness, weight, admission diagnosis, time on mechanical ventilation, neuromuscular disease, presence of multidrug resistant bacterial infection, and renal replacement therapy. This model had an area under receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of 0.75 (95% CI: 0.70–0.79). In addition, the presence of CCCs (odds ratio 25.3, 95% CI: 3.17–201) and the use of technology assistance (odds ratio 4.06, 95% CI: 1.45–11.4) were significantly associated with 2 or more readmissions.
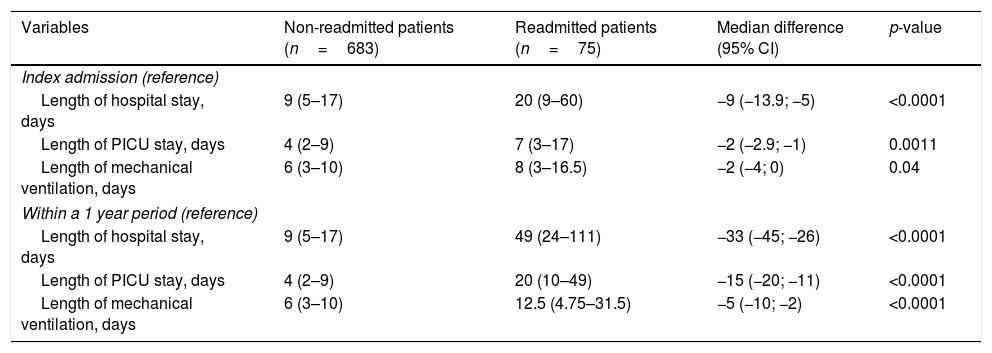
OutcomesThe use of resources, expressed as the number of patients requiring mechanical ventilation and renal replacement therapy, was higher among readmitted patients compared with those non-readmitted (Table 1). The index admission of readmitted patients compared to non-readmitted patients had longer mechanical ventilation time and longer PICU and hospital stays (Table 2).
Outcomes of PICU patients and their index admissions by readmission status.
| Variables | Non-readmitted patients (n=683) | Readmitted patients (n=75) | Median difference (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index admission (reference) | ||||
| Length of hospital stay, days | 9 (5–17) | 20 (9–60) | −9 (−13.9; −5) | <0.0001 |
| Length of PICU stay, days | 4 (2–9) | 7 (3–17) | −2 (−2.9; −1) | 0.0011 |
| Length of mechanical ventilation, days | 6 (3–10) | 8 (3–16.5) | −2 (−4; 0) | 0.04 |
| Within a 1 year period (reference) | ||||
| Length of hospital stay, days | 9 (5–17) | 49 (24–111) | −33 (−45; −26) | <0.0001 |
| Length of PICU stay, days | 4 (2–9) | 20 (10–49) | −15 (−20; −11) | <0.0001 |
| Length of mechanical ventilation, days | 6 (3–10) | 12.5 (4.75–31.5) | −5 (−10; −2) | <0.0001 |
Data are expressed as median (percentile 25, percentile 75).
CI, confidence interval; PICU, pediatric intensive care unit.
Mann–Whitney test.
Also, the first readmission (within 365 days) compared to the index admission of non-readmitted patients presented overall median days spent on mechanical ventilation, PICU, and hospital stays of 12.5 vs 6 days (p<0.001), 20 vs 4 days (p<0.001) and 49 vs 9 days (p<0.001), respectively (Table 2).
The PICU mortality for overall index admissions was 5.1% (n=42) versus 21.3% (n=16) for readmissions within 1 year (p=0.001).
DiscussionPrevious pediatric studies have reported a 1-year occurrence rate of rehospitalization ranging from 17%19 to 22%.17 Compared with a recent North American multicenter study7 assessing PICU readmissions within 1-year, our rate of readmissions (9.8% vs 11%), as well as the rate of patients requiring two or more PICU readmissions (2.5% vs 3.4%) were similar. In contrast, while those authors report a median time to readmission of 30 days, we found a longer interval to the first PICU readmission, with a median of 73 days to readmission. This finding suggests that the use of the 30-day readmission metric as a quality measure20,21 may underestimate an important group of patients requiring high use of resources; this is in line with other investigations that showed that the majority of rehospitalizations experienced by children would not be accounted using the recommended 30-day hospital readmission metrics.17,22
In our study, we identified that more than half of PICU patients were readmitted due to a new condition. This finding may imply that the use of a longer time frame to evaluate readmissions makes it possible to include those readmissions inherent to the condition that generated the index admission, as well as those caused by conditions not related to the previous admission, improving the assessment of complications related to outpatient care.
The main differences between patients with a single admission and those with readmissions were factors associated with medical complexity such as degree of cognitive disability, CCCs and use of technology assistance. By assessing functionality at PICU index admission, we observed that increased cognitive disability was associated with increasing odds of readmission. This finding is similar to that reported elsewhere,6 and it suggests that patients with disabilities are particularly vulnerable to unmet health care needs as demonstrated in studies focusing on hospital readmissions.17 We also found that 65% of patients with a chronic condition in the index admission required at least one readmission. Additionally, we verified that CCC was a strong predictor associated with multiple (two or more) PICU readmissions (odds ratio: 25.3). This finding is in agreement with pediatric studies showing that CCCs and the number of CCCs were associated with rehospitalization17,23 and PICU readmissions,7 and it contrasts with Edwards et al.,7 who reported that most patients, even those with CCC, did not experience a readmission within 1 year.
We also found that the vast majority of patients with CCC had technology dependence (75.7%), which in turn was associated with readmissions. It is noteworthy that children with ≥1 CCC often have functional limitations and special health care needs, including neurologic impairment and technology dependence,24 and they account for nearly 10% of hospital admissions and up to 40% of hospital days and charges.24
From the clinical perspective, one could assume that an important initial step in reducing the number of PICU readmissions would be to proper identify patients who are most likely to be readmitted. According to our results, patients with CCCs, severe cognitive disability, and with technology assistance compose a vulnerable population with higher risk of readmission, for whom targeted interventions are critical. We should mention that between 40 and 50 percent of the readmissions may be associated to social factors and lack of access to community resources.25 In fact, lower educational levels, lower income, and increased distance from the hospital/rural location have been associated to a higher risk of rehospitalization26: therefore, we expected that our rate of readmission would be higher, considering that we take care of a population of lower educational level and limited resources.
Readmissions within 48–72h presumably reflect decision-making at the PICU level, particularly related to transfer criteria; thus, they would be more responsive to PICU-related interventions.1,6 Given that our patients were mostly readmitted after a longer period from index admission, we were not able to analyze which PICU decisions’ interventions would potentially impact the readmission rate.
From another perspective, patients may have diagnoses that wax and wane or recur despite optimal PICU care and clinical assessment. Thus, it is possible that many readmissions represent a consequence of medical complexity – which is especially true for patients with CCCs – rather than a failure of care. In this scenario, the “need” for ICU readmission could identify a very high-risk subgroup of patients at increased risk of poor outcomes, rather than solely identify a poor-quality post-ICU medical care.27 Further studies are necessary to determine if interventions – and which ones – will lower the risk of subsequent admissions for those high-risk patients.
As it might be expected,7,10,17 we identified worsened outcomes among the readmitted group of patients, as those patients had longer duration of mechanical ventilation as well as length of PICU and hospital stays. While there is little disagreement that readmissions are costly to PICUs from both the financial and resource-use perspectives, there is concern that these resources are being wasted in uselessly prolonging the treatment of patients with a very poor prognosis. Nevertheless, we are unable to draw any conclusion from our data.
Our study has some strength. Firstly, previous studies have tried to identify patient groups at risk for readmission but have used administrative databases that lack the qualitative data necessary to be applicable to individual institutions. We evaluated data that were collected prospectively and aggregated several risk factors that would be potentially associated with repeated PICU admissions. Secondly, studies of PICU readmissions have addressed early unplanned readmissions and their modifiable factors, while ours addressed short- and long-term readmissions.1,3–6
The limitations of our study warrant consideration. Firstly, this is a single-center study – therefore, our results may not be generalizable to other types of institutions and other countries, where healthcare systems, social, educational and economic profiles, criteria for PICU admission and discharge, and patient characteristics may vary substantially from our cohort study. Secondly, we only included readmissions and deaths that occurred in our institution, and thus this may have led to an undercounting of readmission. However, patients were likely to be referred to our institution as our PICU is the only tertiary PICU for the region.
In summary, this study showed that a small cohort of readmitted PICU patients within 1 year of an index admission is a major contributor to the use of bed care days. Those patients are likely to have a greater burden of comorbid illness, poor functional status, and need for technology assistance. Additionally, they are prone to having poorer outcomes and higher mortality. Moreover, our findings support the idea that using the traditional 30-day index of readmission may be inadequate to mirror the burden of readmission to PICUs. Therefore, the early identification of those patients and the adequate outpatient follow-up before they accumulate multiple admissions could potentially mitigate the resource usage related to hospitalizations. Nevertheless, the complexity of those children requires high-quality discharge planning – which includes the participation of primary care providers – to ensure a safe transition from the hospital and to make the post-discharge follow-up of those patients actually possible.
Our findings might not be generalized to the private health care system with more available resources. In fact, a long-term management within pediatric homes allows the reduction of hospitalization among medically complex patients such as children with neuromuscular CCCs and those in need of technology assistance.28 Future multicenter studies focusing on risk factors among a larger population are required to identify potential modifiable factors and to develop targeted interventions to improve the outcomes of these critically ill children.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Silva PS, Fonseca MC. Which children account for repeated admissions within 1 year in a Brazilian pediatric intensive care unit? J Pediatr (Rio J). 2019;95:559–66.
Study conducted at Hospital do Servidor Público Municipal, Unidade de Terapia Intensiva Pediátrica, São Paulo, SP, Brazil.