To evaluate the vitamin A status in serum and colostrum of postpartum women with different socioeconomic status, comparing the colostrum retinol supply with the vitamin A requirement of the newborn.
MethodsCross-sectional study conducted with 424 postpartum women. Vitamin A maternal dietary intake was estimated using a food frequency questionnaire. Colostrum and serum retinol levels were measured by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Serum retinol concentrations <20μg/dL were indicative of vitamin A deficiency (VAD). Vitamin A levels provided by colostrum <400μgRAE/day were considered as insufficient for term newborns.
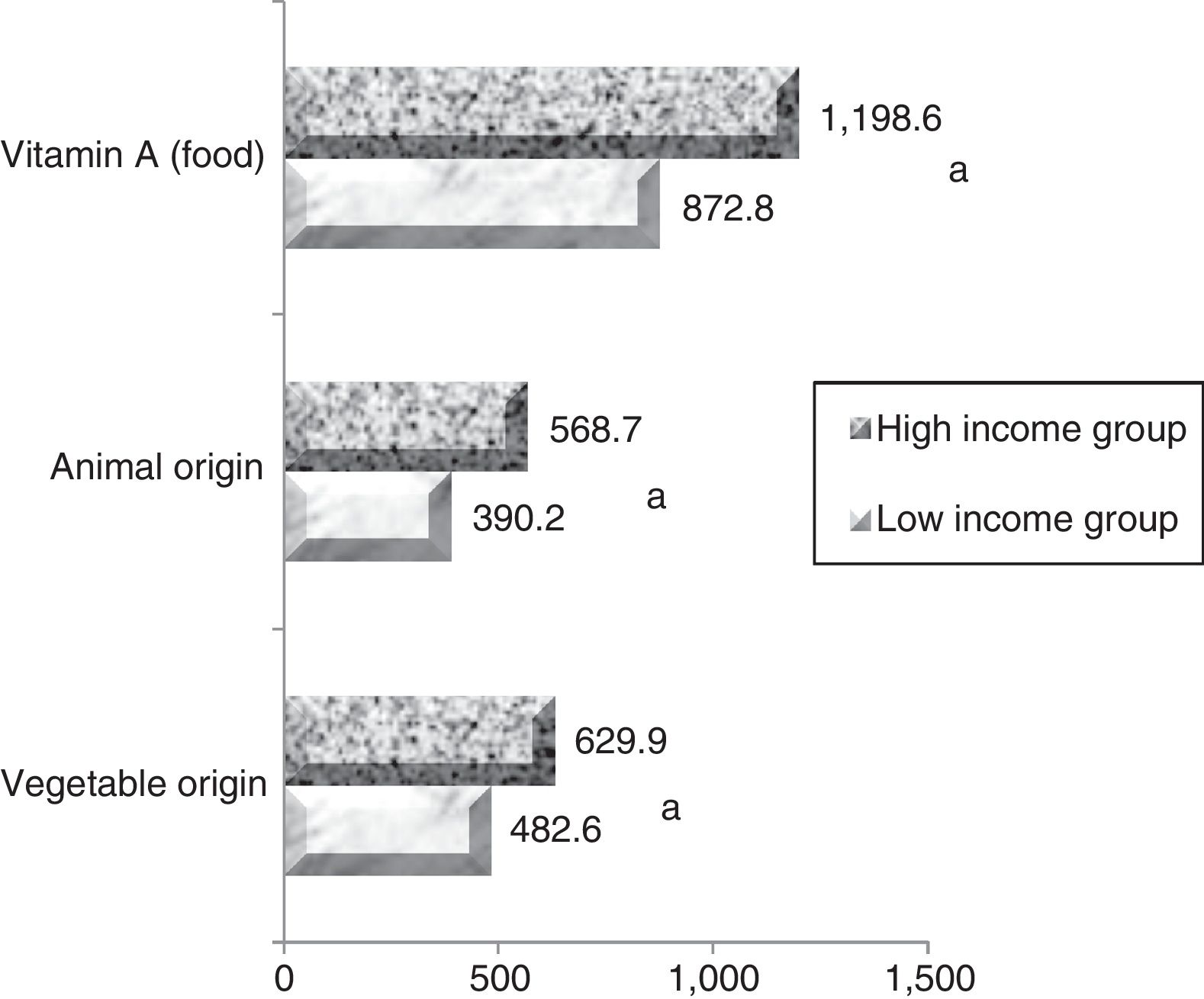
ResultsThe mean maternal vitamin A intake during pregnancy was 872.2±639.2μgRAE/day in low-income women and 1169.2±695.2μgRAE/day for high-income women (p<0.005). The prevalence of vitamin A deficiency was 6.9% (n=18) in the low-income group and 3.7% (n=6) in the high-income group. The estimated mean retinol intake by infants of the high- and low-income mothers were 343.3μgRAE/day (85.8% AI) and 427.2μgRAE/day (106.8% AI), respectively.
ConclusionsSerum vitamin A deficiency was considered a mild public health problem in both populations; however, newborns of low-income women were more likely to receive lower retinol levels through colostrum when compared with newborns of high-income mothers.
Avaliar o estado nutricional de vitamina A no soro e colostro de puérperas com diferentes condições de renda, comparando os níveis de retinol fornecido através do colostro com a necessidade de vitamina A do recém-nascido.
MétodosEstudo transversal com 424 mulheres pós-parto. A ingestão de vitamina A dietética pelas mães foi estimada através de um questionário de frequência do consumo alimentar. Os níveis retinol no soro e colostro foram quantificados por cromatografia líquida de alta eficiência (CLAE). Concentrações de retinol <20μg/dL no soro foram indicativas de vitamin A deficiency. Os níveis de vitamina A fornecidas pelo colostro < 400μg/RAE/dia foram considerados insuficientes para os recém-nascidos a termo.
ResultadosA ingestão média de vitamina A das mães durante a gravidez foi de 872,2±639,2μgRAE/dia em mulheres de baixa renda e 1169,2±695,2μgRAE/dia em mulheres de alta renda (p<0,005). A prevalência de vitamin A deficiency foi de 6,9% (n=18) no grupo de baixa renda e de 3,7% (n=6) no grupo de alta renda. A estimativa dos valores médios de ingestão de retinol por lactentes de mães de baixa e alta renda foi de 343,3μg/RAE/dia (85,8% AI) e 427,2μg/RAE/dia (106,8% AI), respectivamente.
ConclusõesA vitamin A deficiency no soro foi prevalente em ambas as populações, entretanto, recém-nascidos de mães de baixa renda foram mais propensos a receberem níveis inferiores de retinol no colostro em comparação com recém-nascidos de mães de alta renda.
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines vitamin A deficiency (VAD) as tissue concentrations of vitamin A low enough to have adverse health consequences. Serum retinol concentrations below 0.70μmolL−1 indicate deficiency, especially when clinical signs are present, ranging from nyctalopia to blindness.1,2 Worldwide, 19 million pregnant women have low serum retinol, mainly in regions at risk such as Brazil, where 15.3% of the population has been diagnosed as vitamin A deficient.3 The main risk factors attributed to this nutritional deficiency are low income and lack of access to dietary sources of vitamin A.4–6 VAD affects the anatomical and functional integrity of the gastrointestinal and respiratory mucous membranes, significantly increasing maternal morbidity and mortality from infectious diseases.7 Due to the diminished vitamin A body reserves at birth, human milk is responsible for providing adequate amounts of retinoids to ensure normal growth and development.8 Human milk is the ideal source of vitamin A, favoring rapid growth and acting as an antioxidant and immune barrier; however, many factors modulate the composition of this nutrient in breast milk, such as diet, economic status, and maternal nutritional status.9,10
For decades, studies have indicated the public health importance of VAD in pregnant and postpartum women from developing countries,3,11,12 where the extent of the problem in low-income women is evident. However, limited research has been conducted on this deficiency in high-income women.
In Brazil, low-income women frequently attend public hospitals, which routinely distribute supplements of iron salts and folic acid to pregnant women during prenatal care, as required by Ordinance No. 730 issued on May 13, 2005.13 Regarding vitamin A, women receive a single 200,000IU dose of retinyl palmitate in the hospital right after delivery. This strategy applies to all municipalities of the Northeast and North regions of Brazil, as well as to the Legal Amazon, Special Indigenous Sanitary Districts, and municipalities covered by the ‘Brazil without Misery’ plan in the Central-West, South, and Southeast regions.14 In contrast, high-income women attending private hospitals do not receive the supplements provided by the Brazilian Ministry of Health, so obstetricians routinely prescribe daily supplements of vitamin A during pregnancy.
Thus, strategies for preventing VAD in the Brazilian population are different, and the determining factors for VAD in this population need further clarification. The hypothesis established for this study was that high-income mothers who received supplementation during pregnancy would present an adequate vitamin A status, and would therefore offer sufficient amounts of this vitamin through colostrum to meet the nutritional needs of the newborn, when compared with economically deprived woman in Brazil. Thus, the present study is a novel investigation that aimed to assess the vitamin A nutritional status in high- and low-income postpartum women, based on serum and colostrum retinol concentrations, and to compare the retinol levels provided by colostrum with the vitamin A requirements of the newborn.
Material and methodsIn order for the selected sample to be representative, to the authors opted for a probability study using stratified random sampling with proportionate allocation of women by stratum (public and private hospitals). The minimum sample size no should consist of 400 women for the whole group, representing the study city in number of deliveries with live births, considering a 95% confidence level (1−α) and assuming a sampling error of 0.05. Sample size was calculated using the statistical package G*Power (G Power, versão V.3.1.7, Dusseldorf, Germany).15
The sample was calculated based on the ratio of births to live births between 2008 and 2011 registered by the Epidemiological Surveillance of Rio Grande do Norte/Brazil, totaling 17,775 births. The study included public and private hospitals, with a significant number of births, from four regions (north, south, east, and west; n=424). Public hospitals had 61.8% of representativeness (n=262) and private hospitals had 38.2% (n=162). The participants were recruited at the maternity ward by random sampling.
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil, under protocol number CAAE: 09775312.5.0000.5537. Women enrolled in the study were informed about the research objectives and signed an informed consent prior to their inclusion.
The sample included healthy adolescent and adult women, who used or used not supplements containing vitamin A during pregnancy, single gestation and full-term delivery (≥37 weeks of gestation) without malformations. Women with clinical conditions (cancer, heart disease, diabetes, gastrointestinal, liver and kidney diseases, infectious diseases, and who underwent gastroplasty surgery), multiple pregnancy, and preterm delivery were excluded.
The individuals selected for each population stratum were recruited within 24–48h after delivery through a simple random sampling using the hospital records, so that each postpartum woman in each stratum had an equal probability of being selected. Socioeconomic data were collected by interview. The data collection instrument used was a questionnaire designed for this study.
From participant-reported family income information and number of residents in their homes, household income per capita was calculated as a standard composite indicator of life conditions and divided into two categories: (<1 minimum wage) and (>2 minimum wages), representing the “low-income” and “high-income” groups, respectively, as recommended by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics.16 Mothers were also asked about age, years of education, use of supplements containing vitamin A, and whether they received professional nutritional guidance during pregnancy. Furthermore, they were asked whether they knew which foods were good vitamin A sources and, in case of positive responses, they were immediately assessed by a trained interviewer to assess their knowledge on the subject. Anthropometric data of women and children were collected from the Mother–Child Protection Card and hospital records.
A food-frequency questionnaire (FFQ) was used to assess the last trimester of pregnancy.17 FFQ data were analyzed by the software Avanutri (Avanutri®, model 4.0, RJ, Brazil).18 Questionnaire data were transformed into amount of daily intake by multiplying the standard portion of the questionnaire by the number of consumed portions; the result was then divided by the number of days included in the time interval quoted (weekly, monthly, semi-annual, and annual). Avanutri presents the vitamin A content in foods as microgram of retinol equivalent (μgRE); besides, it presents the pro-vitamin A content in vegetable sources as retinol activity equivalents (RAE) and converts it to μgRE by dividing it by 2, following the IOM's recommendation (1 retinol activity equivalent=1μg of all-trans retinol).19
Vitamin A values were compared with the estimated average requirement (EAR) for pregnant adults most commonly recommended in population studies. The daily average intake for pregnant women between 19 and 50 years old is equivalent to 550μg RAE/day; for those aged ≤18 years old, the value is equivalent to 530μgRAE/day. A vitamin A dietary intake lower than the these values was considered as poor intake.19
Paired samples of serum and breast milk were collected at the hospital after an overnight fasting, immediately before vitamin A mega-dose administration (low-income women attending public hospitals). Colostrum milk samples (500μL) were collected through manual expression of a single breast, at the beginning and end of the breastfeeding. Blood samples (5mL) were collected by venipuncture. The samples were stored in light-proof polypropylene tubes and immediately transported under refrigeration to the biochemistry and nutrition research laboratory.
The blood samples were centrifuged for 10min (500×g) to collect 1000μL of serum from each sample. The serum was protected from direct light and stored at −20°C until retinol could be extracted, as recommended by Ortega et al.20 Retinol was extracted from colostrum samples according to the adapted method of Giuliano et al.21 The extracts were dissolved in 500μL of absolute ethanol (Vetec, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) and 60μL were analyzed in the HPLC equipment.
To estimate the prevalence of VAD, the resulting serum retinol concentrations were compared with the cut-off point of <0.70μmolL−1.3 The prevalence of VAD was classified according to the categories of public health importance established by the WHO (2009): prevalence<2% (no public health problem); 2%<prevalence<10% (mild public health problem); 10%<prevalence<20% (moderate public health problem); and prevalence>20% (severe public health problem).3
To assess the provision of vitamin A by colostrum, in comparison to the nutritional requirement of the newborn, it was considered a daily intake of 396mL of milk22 by newborn infants; the resulting values were compared with the adequate intake (AI) of vitamin A: 400μgRAE/day for children aged 0–6 months.19
Statistical analyzes were performed using SPSS (SPSS for Windows, version 20.0. IL, USA). The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test coupled with Gauss curve was used for assessing the normality of the retinol values. The descriptive analysis was performed using mean, standard deviation, and percentage for continuous variables. Categorical variables were analyzed by the chi-squared test. Mean comparisons were performed using Student's t-test for independent samples and analysis of variance (ANOVA). For the association between the prevalence of deficient vitamin A levels in serum and breastmilk with household income, the risk prevalence (RP) was used. A bivariate logistic model was used, and the response variable was the retinol concentration (μg/dL), while the explanatory variables were: age, marital status, mother's years of education, vitamin A supplementation during pregnancy, and maternal pre-pregnancy weight. In all cases, two-tailed analyzes were performed and considered statistically significant when p<0.05.
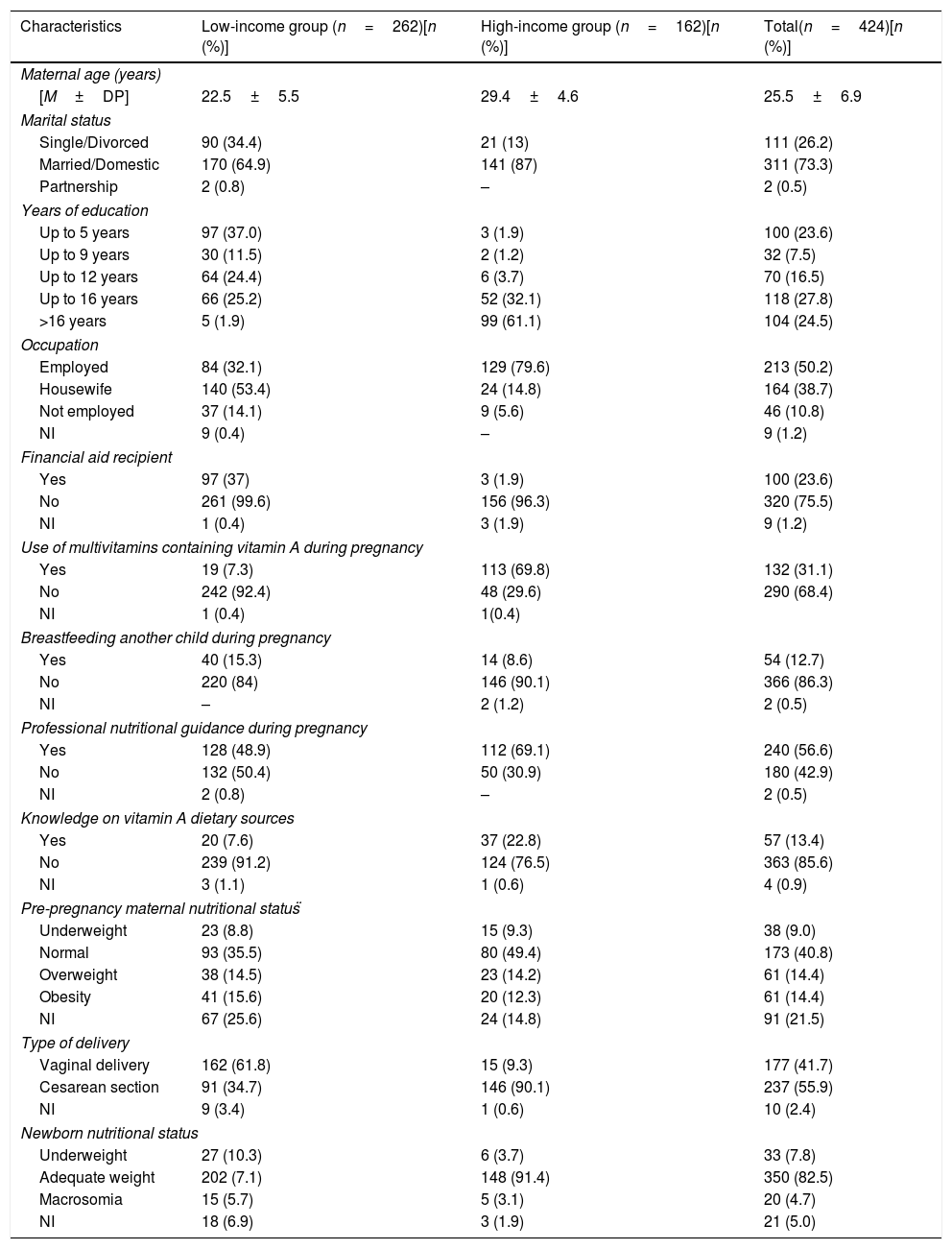
ResultsThe random selection of mothers resulted in 424 postpartum women enrolled in the study. A total of 82 women met the study criteria, but were not included in the sample due to participation refusal or insufficient/impaired biological material collection. Maternal characteristics of each sample stratum (high- and low-income mothers) are presented in Table 1.
General characteristics of the low- and high-income women enrolled in the study attending public and private maternity hospitals in Natal, RN, Brazil.
| Characteristics | Low-income group (n=262)[n (%)] | High-income group (n=162)[n (%)] | Total(n=424)[n (%)] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal age (years) | |||
| [M±DP] | 22.5±5.5 | 29.4±4.6 | 25.5±6.9 |
| Marital status | |||
| Single/Divorced | 90 (34.4) | 21 (13) | 111 (26.2) |
| Married/Domestic | 170 (64.9) | 141 (87) | 311 (73.3) |
| Partnership | 2 (0.8) | – | 2 (0.5) |
| Years of education | |||
| Up to 5 years | 97 (37.0) | 3 (1.9) | 100 (23.6) |
| Up to 9 years | 30 (11.5) | 2 (1.2) | 32 (7.5) |
| Up to 12 years | 64 (24.4) | 6 (3.7) | 70 (16.5) |
| Up to 16 years | 66 (25.2) | 52 (32.1) | 118 (27.8) |
| >16 years | 5 (1.9) | 99 (61.1) | 104 (24.5) |
| Occupation | |||
| Employed | 84 (32.1) | 129 (79.6) | 213 (50.2) |
| Housewife | 140 (53.4) | 24 (14.8) | 164 (38.7) |
| Not employed | 37 (14.1) | 9 (5.6) | 46 (10.8) |
| NI | 9 (0.4) | – | 9 (1.2) |
| Financial aid recipient | |||
| Yes | 97 (37) | 3 (1.9) | 100 (23.6) |
| No | 261 (99.6) | 156 (96.3) | 320 (75.5) |
| NI | 1 (0.4) | 3 (1.9) | 9 (1.2) |
| Use of multivitamins containing vitamin A during pregnancy | |||
| Yes | 19 (7.3) | 113 (69.8) | 132 (31.1) |
| No | 242 (92.4) | 48 (29.6) | 290 (68.4) |
| NI | 1 (0.4) | 1(0.4) | |
| Breastfeeding another child during pregnancy | |||
| Yes | 40 (15.3) | 14 (8.6) | 54 (12.7) |
| No | 220 (84) | 146 (90.1) | 366 (86.3) |
| NI | – | 2 (1.2) | 2 (0.5) |
| Professional nutritional guidance during pregnancy | |||
| Yes | 128 (48.9) | 112 (69.1) | 240 (56.6) |
| No | 132 (50.4) | 50 (30.9) | 180 (42.9) |
| NI | 2 (0.8) | – | 2 (0.5) |
| Knowledge on vitamin A dietary sources | |||
| Yes | 20 (7.6) | 37 (22.8) | 57 (13.4) |
| No | 239 (91.2) | 124 (76.5) | 363 (85.6) |
| NI | 3 (1.1) | 1 (0.6) | 4 (0.9) |
| Pre-pregnancy maternal nutritional status̈ | |||
| Underweight | 23 (8.8) | 15 (9.3) | 38 (9.0) |
| Normal | 93 (35.5) | 80 (49.4) | 173 (40.8) |
| Overweight | 38 (14.5) | 23 (14.2) | 61 (14.4) |
| Obesity | 41 (15.6) | 20 (12.3) | 61 (14.4) |
| NI | 67 (25.6) | 24 (14.8) | 91 (21.5) |
| Type of delivery | |||
| Vaginal delivery | 162 (61.8) | 15 (9.3) | 177 (41.7) |
| Cesarean section | 91 (34.7) | 146 (90.1) | 237 (55.9) |
| NI | 9 (3.4) | 1 (0.6) | 10 (2.4) |
| Newborn nutritional status | |||
| Underweight | 27 (10.3) | 6 (3.7) | 33 (7.8) |
| Adequate weight | 202 (7.1) | 148 (91.4) | 350 (82.5) |
| Macrosomia | 15 (5.7) | 5 (3.1) | 20 (4.7) |
| NI | 18 (6.9) | 3 (1.9) | 21 (5.0) |
NI, not informed; –, data from the first appointment of prenatal care.
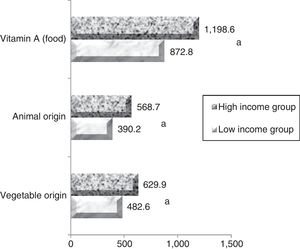
The mean maternal vitamin A intake during pregnancy was 872.2±639.2μgRAE/day in the low-income group and 1169.2±695.2μgRAE/day in the high-income group (p<0.005). Individually assessing the population, it was observed that 38.4% (n=100) and 17.3% (n=28) of women in low- and high-income groups, respectively, had dietary vitamin A intake below the ideal amount for this stage of life (=530μg/day for ≤18 years old individuals, and=550μg/day for adults), evidencing that the low-income group was more likely to develop VAD when compared with the high-income group. Regarding the vitamin A food sources, vegetable sources (pro-vitamin A) contributed to more than 52% of the mean consumption in the low-income group and over 55.2% in the high-income group. The values for vitamin A intake are shown in Fig. 1.
Regarding the serum retinol concentrations in low- and high-income mothers, the groups presented averages of 39.8±12.7μg/dL and 45.4±13.4μg/dL respectively, presenting a highly significant difference (p<0.0001). The prevalence of VAD in the low-income group was 6.9% (n=18) and 3.7% (n=6) in the high-income group (RP 1.9; 95% CI: 0.7–4.9).
The low- and high-income groups presented mean retinol levels in colostrum of 86.7±40.0μg/dL and 107.9±58.6μg/dL respectively, a highly significant difference (p<0.0001). Comparing retinol levels provided through colostrum with the nutritional needs of the newborn AI 400μg/RAE/day) and considering a daily consumption of 396mL of milk/day through exclusive breastfeeding (from 0 to 6 months), only infants in the high-income group received retinol levels higher than the AI. The estimated retinol intakes by infants in the high- and low-income groups were 343.3μg/RAE/day (85.8% AI) and 427.2μg/RAE/day (106.8% AI), respectively.
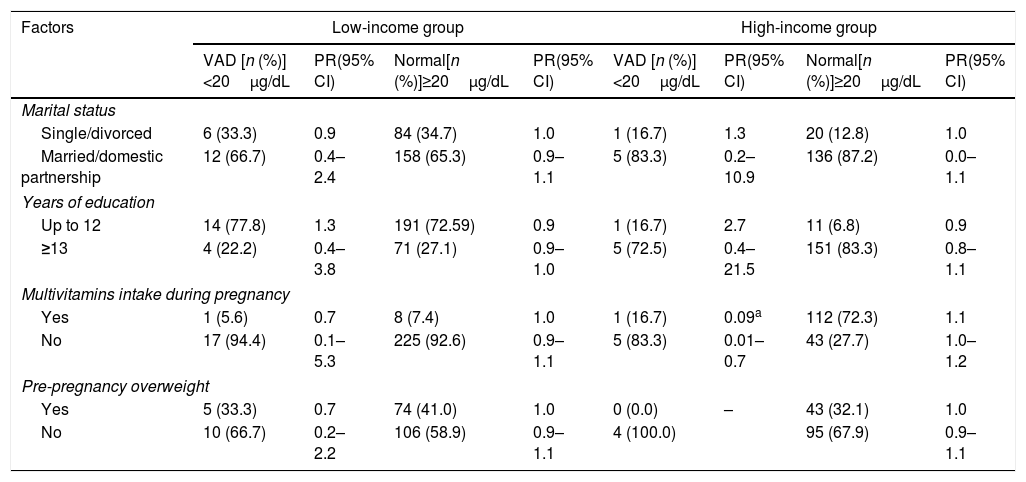
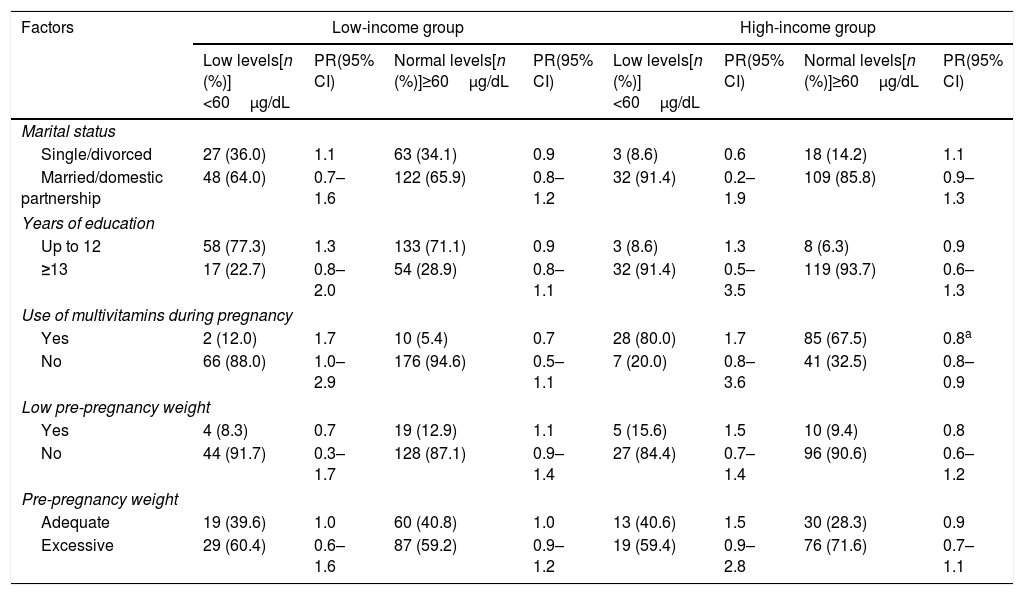
In the bivariate logistic analysis to estimate the influence of social and health variables on vitamin A status, the following variables were included: marital status, years of education, use of multivitamins during pregnancy, and pre-pregnancy nutritional status. In the final model, statistically significant association was found only between the variable “use of multivitamins during pregnancy” and adequate levels of vitamin A in serum (RP 0.09; 95% CI: 0.01–0.7) and colostrum (RP 0.8; 95% CI: 0.9–0.9), revealing this variable as a protective factor present in the high-income group. No associations were observed between the other variables and vitamin A levels in serum and colostrum (Tables 2 and 3).
Potential factors associated with the deficiency or adequacy of vitamin A status in serum of low- and high-income mothers.
| Factors | Low-income group | High-income group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAD [n (%)]<20μg/dL | PR(95% CI) | Normal[n (%)]≥20μg/dL | PR(95% CI) | VAD [n (%)]<20μg/dL | PR(95% CI) | Normal[n (%)]≥20μg/dL | PR(95% CI) | |
| Marital status | ||||||||
| Single/divorced | 6 (33.3) | 0.9 | 84 (34.7) | 1.0 | 1 (16.7) | 1.3 | 20 (12.8) | 1.0 |
| Married/domestic partnership | 12 (66.7) | 0.4–2.4 | 158 (65.3) | 0.9–1.1 | 5 (83.3) | 0.2–10.9 | 136 (87.2) | 0.0–1.1 |
| Years of education | ||||||||
| Up to 12 | 14 (77.8) | 1.3 | 191 (72.59) | 0.9 | 1 (16.7) | 2.7 | 11 (6.8) | 0.9 |
| ≥13 | 4 (22.2) | 0.4–3.8 | 71 (27.1) | 0.9–1.0 | 5 (72.5) | 0.4–21.5 | 151 (83.3) | 0.8–1.1 |
| Multivitamins intake during pregnancy | ||||||||
| Yes | 1 (5.6) | 0.7 | 8 (7.4) | 1.0 | 1 (16.7) | 0.09a | 112 (72.3) | 1.1 |
| No | 17 (94.4) | 0.1–5.3 | 225 (92.6) | 0.9–1.1 | 5 (83.3) | 0.01–0.7 | 43 (27.7) | 1.0–1.2 |
| Pre-pregnancy overweight | ||||||||
| Yes | 5 (33.3) | 0.7 | 74 (41.0) | 1.0 | 0 (0.0) | – | 43 (32.1) | 1.0 |
| No | 10 (66.7) | 0.2–2.2 | 106 (58.9) | 0.9–1.1 | 4 (100.0) | 95 (67.9) | 0.9–1.1 | |
VAD, vitamin A deficiency; n, number of mothers presenting poor or adequate retinol levels according to the characteristics mentioned for each group; %, percentage of mothers presenting poor or adequate retinol levels according to the characteristics mentioned for each group; PR, prevalence of risk; (95%), 95% confidence interval; –, did not have sufficient n in one of the characteristics to perform statistical analysis.
Potential factors associated with the deficiency or adequacy of vitamin A status in colostrum of low- and high-income mothers.
| Factors | Low-income group | High-income group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low levels[n (%)]<60μg/dL | PR(95% CI) | Normal levels[n (%)]≥60μg/dL | PR(95% CI) | Low levels[n (%)]<60μg/dL | PR(95% CI) | Normal levels[n (%)]≥60μg/dL | PR(95% CI) | |
| Marital status | ||||||||
| Single/divorced | 27 (36.0) | 1.1 | 63 (34.1) | 0.9 | 3 (8.6) | 0.6 | 18 (14.2) | 1.1 |
| Married/domestic partnership | 48 (64.0) | 0.7–1.6 | 122 (65.9) | 0.8–1.2 | 32 (91.4) | 0.2–1.9 | 109 (85.8) | 0.9–1.3 |
| Years of education | ||||||||
| Up to 12 | 58 (77.3) | 1.3 | 133 (71.1) | 0.9 | 3 (8.6) | 1.3 | 8 (6.3) | 0.9 |
| ≥13 | 17 (22.7) | 0.8–2.0 | 54 (28.9) | 0.8–1.1 | 32 (91.4) | 0.5–3.5 | 119 (93.7) | 0.6–1.3 |
| Use of multivitamins during pregnancy | ||||||||
| Yes | 2 (12.0) | 1.7 | 10 (5.4) | 0.7 | 28 (80.0) | 1.7 | 85 (67.5) | 0.8a |
| No | 66 (88.0) | 1.0–2.9 | 176 (94.6) | 0.5–1.1 | 7 (20.0) | 0.8–3.6 | 41 (32.5) | 0.8–0.9 |
| Low pre-pregnancy weight | ||||||||
| Yes | 4 (8.3) | 0.7 | 19 (12.9) | 1.1 | 5 (15.6) | 1.5 | 10 (9.4) | 0.8 |
| No | 44 (91.7) | 0.3–1.7 | 128 (87.1) | 0.9–1.4 | 27 (84.4) | 0.7–1.4 | 96 (90.6) | 0.6–1.2 |
| Pre-pregnancy weight | ||||||||
| Adequate | 19 (39.6) | 1.0 | 60 (40.8) | 1.0 | 13 (40.6) | 1.5 | 30 (28.3) | 0.9 |
| Excessive | 29 (60.4) | 0.6–1.6 | 87 (59.2) | 0.9–1.2 | 19 (59.4) | 0.9–2.8 | 76 (71.6) | 0.7–1.1 |
n, number of mothers presenting poor or adequate retinol levels according to the characteristics mentioned for each group; %, percentage of mothers presenting poor or adequate retinol levels according to the characteristics mentioned for each group; PR, prevalence of risk; (95%), 95% confidence interval; –, did not have sufficient n in one of the characteristics to perform statistical analysis.
In Brazil, the low-income population uses the public health care system, while the private system is mostly used by high-income individuals. Dividing the study population into two groups according to per capita income, the mean retinol concentrations among low- and high-income women presented highly significant differences.
Both low- and high-income groups evidenced a mild health problem regarding VAD. This result was expected in low-income women, according to other studies developed with the same population in Brazil and worldwide, especially where this public health problem is still present, such as in African and Latin American countries.6,23,24
Studies assessing the prevalence of VAD in high-income women are scarce; it was unexpected to find a public health problem regarding VAD in this group, since vitamin A intake was 82.7% adequate in this population. However, assessing the dietary sources of vitamin A in this group, it was noticed that 55.2% of vitamin A consumption came from vegetable sources (pro-vitamin A), which rely on enzymatic oxidation to produce active retinol, in addition to numerous intestinal and genetic factors that may influence the efficiency of pro-vitamin A bioconversion into the active form.25 Moreover, 29.6% of these women did not use multivitamins during pregnancy (Table 1), which may explain an occurrence of 3.6% of VAD in this group. In a study that evaluated the effect of different multivitamin types (containing vitamin A) on serum retinol levels during pregnancy, it was found that the supplemented group did not present any cases of deficiency, while the control group presented 12% of deficiency cases.26 Thus, it demonstrates that postpartum women who do not receive supplementation during pregnancy are more likely to develop VAD.
Regarding colostrum retinol levels, a significant difference was observed between the study groups; lower levels were observed in the low-income group, resulting consequently in a lower retinol supply through colostrum, when compared with the minimum recommendation for newborns. Such findings highlight the clinical importance of supplementation for this population during the nursing period, in order to meet the extra vitamin A demand throughout lactation and to avoid extreme VAD in the mother–child dyad. VAD during lactation could affect cellular differentiation, multiple mechanisms of innate immunity, hematopoiesis, and coagulation. Such abnormalities may aggravate infections and anemia or compromise post-surgical recovery from cesarean delivery, leading to morbidity and mortality.24 In newborns, VAD increases the risk of death from infectious and respiratory diseases.27
For low-income women attending public maternity hospitals in Brazil, the interventional measure consists of giving an oral mega-dose containing 60mg (200,000IU) of retinol palmitate to women immediately after delivery, as an intervention to control VAD.13 Considering that the study participants were recruited 24–48h after delivery and their blood samples were collected right before the vitamin A mega-dose administration, the deficiency cases probably existed during pregnancy. Thus, postnatal supplementation is performed to minimize reversible damage to newborns and to partially recover maternal vitamin A status prior to lactation, as it is also during pregnancy that the requirement for vitamin A increases in order to promote optimal growth and maturation of tissues and organs.28 It is worth noting that supplementation at postpartum is an emergency measure and does not solve the core problem.9
The difference found in colostrum retinol levels between the study groups can be justified by the mothers’ dietary intake. The lipoprotein lipase enzyme (LPL) is essential for the uptake of postprandial retinol by the mammary gland through a dynamic mechanism. LPL hydrolyzes retinol esters derived from chylomicrons, allowing the retinol transfer into the alveoli, or it binds to chylomicrons, favoring is internalization through recognition receptors in the cellular surface. That is, in the absence of sufficient retinol provided through diet or supplementation, LPL is impaired in the processing of vitamin A to milk or even to form reserves.29 Thus, the results of this study suggest that the significant difference in the mean concentration of colostrum retinol between high- and low-income groups arises from supplementation with multivitamins containing vitamin A, consumed by 69.8% of the high-income group during pregnancy.
It is worth noting that the results found for retinol levels provided by colostrum in the low-income group do not diminish the importance of neither colostrum nor breast milk, since the calculation was based on the mean intake of milk (mL) suggested by the literature.22 However, if a newborn ingests a volume considerably greater than the suggested, it is likely that the vitamin A requirement will be met, except in cases of extreme maternal deficiency.
Women attending private hospitals do not receive the mega-dose provided by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. The study women attending private hospitals reported that they were advised to take multivitamin and multimineral supplements containing the recommended dietary allowance (RDA; 770μg/day) of vitamin A during pregnancy and to start daily doses of vitamin A in the sixteenth week of gestation. In 2011, the WHO suggested vitamin A supplementation for pregnant women living in endemic areas of deficiency, but emphasized that the daily or weekly dose should not exceed 10,000IU/day and should only be initiated after the 60th day of gestation.30
In this study, a significant association was observed between supplementation with multivitamins and normal vitamin A status in serum and colostrum, suggesting that the intervention prescribed to high-income women attending private maternity hospitals in Brazil is more effective in increasing retinol levels in serum and colostrum milk. This association was expected, since micronutrient supplementation is an obvious strategy to overcome the negative health effects of deficiencies on pregnant women's health and to improve the women's nutritient status for lactation. In light of the aforementioned facts, it is suggested that the current intervention measures against VAD in pregnant Brazilian women should be redesigned, since the present study supports that supplementation with vitamin A-containing multivitamins might be necessary, especially for low-income women normally assisted by the public health system.
FundingThis study was supported by grants from the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
The authors gratefully acknowledge the cooperation of the maternity hospitals for providing data for this survey. They also would like to thank all the women who agreed to participate, providing their biological materials and personal data to this study.
Please cite this article as: Gurgel CS, Grilo EC, Lira LQ, Assunção DG, Oliveira PG, Melo LR, et al. Vitamin A nutritional status in high- and low-income postpartum women and its effect on colostrum and the requirements of the term newborn. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2018;94:207–215.
Study conducted at Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN), Natal, RN, Brazil.