This systematic review aimed to verify the available scientific evidence on the clinical performance and diagnostic accuracy of nutritional screening tools in hospitalized pediatric patients.
Data sourceA search was performed in the Medline (National Library of Medicine United States), LILACS (Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences), PubMed (US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health), in the SCIELO (Scientific Electronic Library Online), through CAPES portal (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), bases Scopus e Web of Science. The descriptors used in accordance with the Descriptors in Health Sciences (DeCS)/Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) list were “malnutrition”, “screening”, and “pediatrics”, as well as the equivalent words in Portuguese.
Summary of the findingsThe authors identified 270 articles published between 2004 and 2014. After applying the selection criteria, 35 were analyzed in full and eight articles were included in the systematic review. We evaluated the methodological quality of the studies using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS). Five nutritional screening tools in pediatrics were identified. Among these, the Screening Tool for the Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics (STAMP) showed high sensitivity, almost perfect inter-rater agreement and between the screening and the reference standard; the Screening Tool Risk on Nutritional Status and Growth (STRONGkids) showed high sensitivity, lower percentage of specificity, substantial intra-rater agreement, and ease of use in clinical practice.
ConclusionsThe studies included in this systematic review showed good performance of the nutritional screening tools in pediatrics, especially STRONGkids and STAMP. The authors emphasize the need to perform for more studies in this area. Only one tool was translated and adapted to the Brazilian pediatric population, and it is essential to carry out studies of tool adaptation and validation for this population.
Esta revisão sistemática tem por objetivo verificar as evidências científicas disponíveis sobre o desempenho clínico e acurácia diagnóstica dos instrumentos de triagem nutricional em pacientes pediátricos hospitalizados.
Fonte de dadosRealizou-se busca nas bases de dados Medline (National Library of Medicine United States), LILACS (Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences), PubMed (US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health), na biblioteca eletrônica SCIELO (Scientific Electronic Library Online), através do portal de periódicos da CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), bases Scopus e Web of Science. Os descritores utilizados conforme lista do DeCS (Descritores em Ciências da Saúde)/MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) foram “desnutrição”, “triagem” e “pediatria”, bem como, “malnutrition”, “screening” e “pediatrics”, respectivamente.
Síntese dos dadosIdentificou-se 270 artigos, publicados entre 2004 e 2014. Após aplicação dos critérios de seleção, 35 foram analisados na íntegra, sendo incluídos 8 artigos na revisão sistemática. Avaliou-se a qualidade metodológica dos estudos utilizando-se o QUADAS (Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies). Verificou-se 05 instrumentos de triagem nutricional em pediatria. Dentre estes, o STAMP (Screening Tool for the Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics) apresentou sensibilidade elevada, concordância quase perfeita inter-avaliador e entre a triagem e padrão de referência; o STRONGkids (Screening Tool Risk on Nutritional Status and Growth) evidenciou sensibilidade elevada, menor percentual de especificidade, concordância intra-avaliador substancial e facilidade de uso na prática clínica.
ConclusõesOs estudos incluídos nesta revisão sistemática demonstraram um bom desempenho dos instrumentos de triagem nutricional em pediatria, principalmente STRONGkids e STAMP. Evidencia-se a necessidade de mais pesquisas nessa área. Apenas um instrumento foi traduzido e adaptado para a população pediátrica brasileira, sendo imprescindível a realização de estudos de adaptação e validação de instrumentos para essa população.
It has been widely described in the literature that inadequate nutritional status has negative implications for the child, resulting in important consequences for the child's health and development.1–3
Malnutrition in pediatric patients is a severe pathological condition and a risk factor for unfavorable outcome. It is associated with immune system vulnerability, increased risk of infections, postoperative complications, impaired wound healing, and development of pressure ulcers, as well as increased morbidity and mortality of the affected individuals.4–8
This clinical condition slows down the recovery process, demanding prolonged hospital stay and increasing costs related to medication and health care.4,5,8,9 Even with the frequent association between hospital malnutrition and risk of adverse clinical events, this is a problem that remains largely underestimated and that sometimes goes unnoticed.3,10–12
In recent decades, within the scenario of the epidemiological and nutritional transition, Brazilian studies have evidenced a significant decrease in the prevalence of child malnutrition in the country.13,14 However, in opposition to a downward trend in malnutrition in the general population, the situation is getting worse in hospitals, as demonstrated by the increase in its incidence15,16 and prevalence.17
Although it is difficult to quantify the actual prevalence of malnutrition in hospitalized children, scientific evidence emphasizes their frequency in this group. International studies show malnutrition rates between 19% and 45.6% in hospitalized children.1,18–20 In Brazil, surveys indicate rates of 18% to 58%.21–24
During hospitalization, children can be malnourished or aggravate a pre-existing malnutrition situation. Therefore, it is essential to achieve the early detection of nutritional depletion during hospital stay.1,25
In this sense, the patient nutritional status assessment identifies only those who are already malnourished, and not those at risk of malnutrition.5,26 To prevent hospital malnutrition, studies show that the early detection of nutritional risk is essential, as it allows appropriate nutritional interventions to prevent malnutrition and its consequences.2,4,5,8,12,27
For adult patients, several screening tools have been validated in a variety of clinical scenarios and with different groups of patients.4 However, appropriate tools for pediatric use are scarce,28,29 and there is no consensus about the best method to assess risk of malnutrition in these patients.1,8,30
Although there are recommendations of several societies to perform nutritional risk identification in pediatric patients,3,31 in practice, due to the lack of a simple and validated method, nutritional screening is not yet widely performed.4,9 Any tool designed for nutritional screening in pediatrics should be simple, fast, reproducible,7 and have good sensitivity and specificity.4,29,32
Therefore, this systematic review aimed to verify the available scientific evidence on the clinical performance and diagnostic accuracy of the tools used for screening malnutrition risk in pediatric patients.
MethodsThis was a systematic review of the literature on the available scientific evidence on the clinical performance and diagnostic accuracy of the tools used for malnutrition risk screening in pediatric patients, published between 2004 and 2014.
The search strategy used included searches in the MEDLINE, LILACS, PubMed, the SciELO electronic library databases; the CAPES Portal was used to access the Scopus and Web of Science databases. The descriptors were chosen according to the Descriptors in Health Sciences (DeCS) and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) list. In accordance with the DeCS list, the used terms were “desnutrição,” “triagem,” and “pediatria” in Portuguese; the MeSH descriptors were “malnutrition,” “screening,” and “pediatrics”, in English. In addition to descriptors, the Boolean operator “AND” was applied for the combination of terms in the databases.
Searches using the references of selected articles were also performed, aiming to identify publications not previously found that were relevant to the review topic. The searches were performed from November 2014 to April 2015.
The following inclusion criteria were defined for adequate article selection: studies on hospitalized pediatric patients, which assessed the use of some nutritional risk screening tool; and articles published in the last decade (2004–2014) in Portuguese, English, and/or Spanish. The exclusion criteria were: qualitative studies, review articles, editorials, letters to the editor, book chapters, articles not available to be accessed in full, and also articles that did not have data on the sensitivity and specificity of the screening tools.
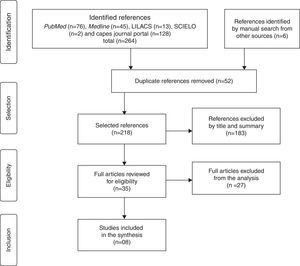
The article selection process was carried out in four stages, according to the model recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration:33 1 – identification of the articles by searching the databases and articles retrieved through the references of selected articles; 2 – selection, at this stage, the duplicate articles were excluded, and by screening the titles and abstracts of the remaining articles, the authors excluded those that had no association with the keywords defined for the search; 3 – the eligibility was assessed by reading the articles in full (excluding those that did not meet the pre-established eligibility criteria) and; 4 – inclusion of eligible articles in the systematic review.
To evaluate the clinical performance and diagnostic accuracy of the tools, the following criteria were considered: sensitivity – screening capacity to detect individuals who were actually at nutritional risk; specificity – the capacity to diagnose individuals with no nutritional risk; positive predictive value – the patient's probability to be at risk among those who tested positive; and negative predictive value – the patient's probability to be healthy among those who tested negative.34
The authors also verified whether the studies analyzed the reproducibility and reliability of the screening tools, using data from the agreement analysis between the assessed nutritional risk screening and the used reference standard, as well as the intra- and inter-bserver agreement shown in the studies. To interpret the Kappa statistical value, the classification of Landis and Koch was considered:35 no agreement (<0); poor agreement (0–0.19); mild agreement (0.20–0.39); moderate agreement (0.40–0.59); substantial agreement (0.60–0.79); and almost perfect agreement (0.80–1.00).
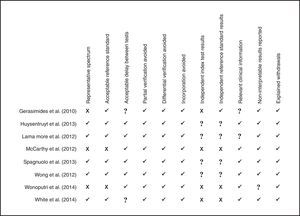
To assess the methodological quality of the studies, a modified version of Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS) was used.36 Recommended by the Cochrane Handbook,37 this tool is designed to measure the sources of bias, variability, and quality of information in the studies.36 This version evaluates 11 of the 14 items of the original version, considering that the remaining items (2, 8, and 9) refer to problems related to how to report data, and not exactly to the methodological quality of the study.38 A good study performance is verified when it has a positive evaluation in at least eight of the 11 items of QUADAS.39
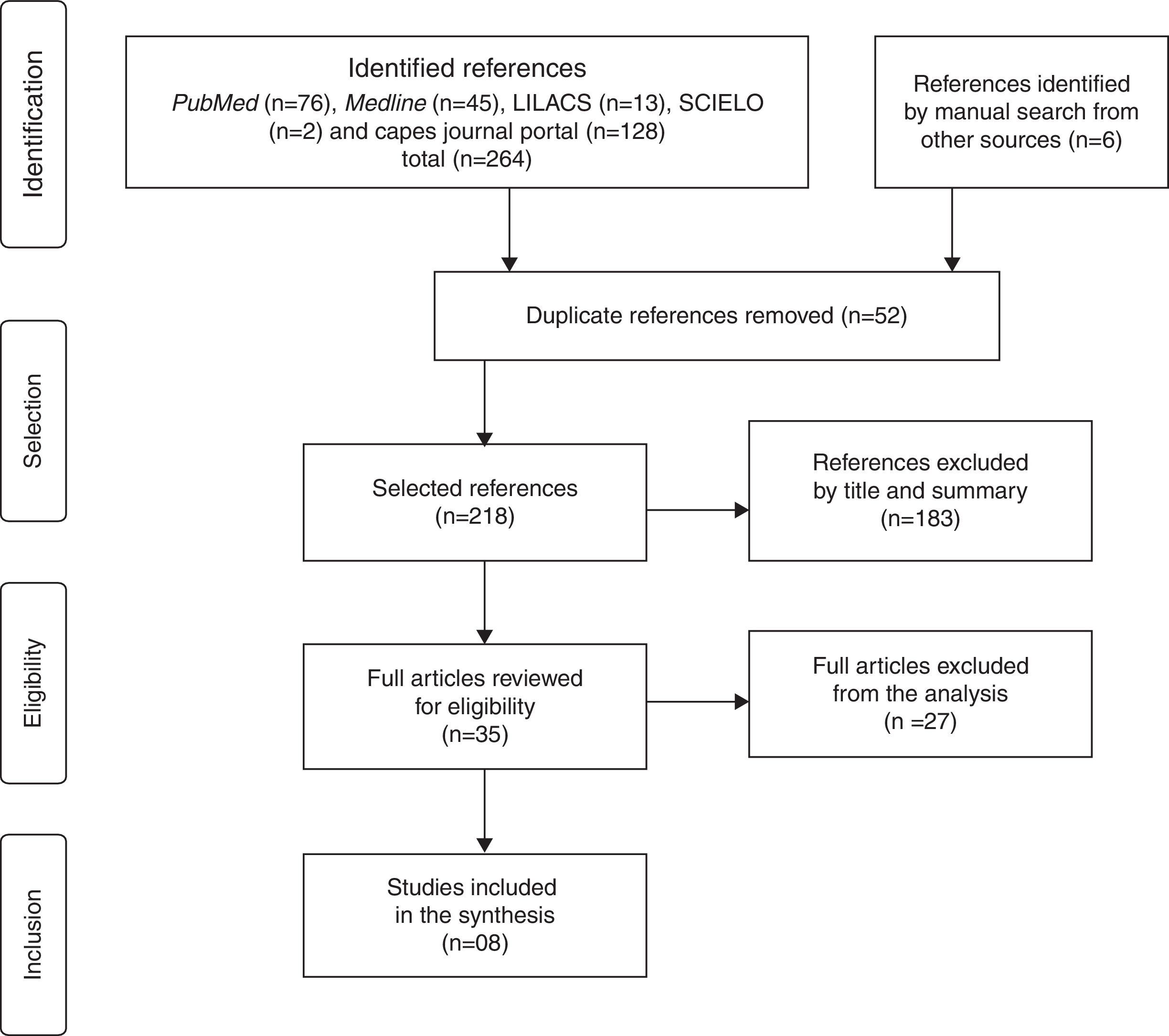
ResultsInitially, 270 articles were identified, and at the end of the selection process, according to the model recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration, eight articles were quantified, which met all the pre-established eligibility criteria and, therefore, were included in this systematic review (Fig. 1).
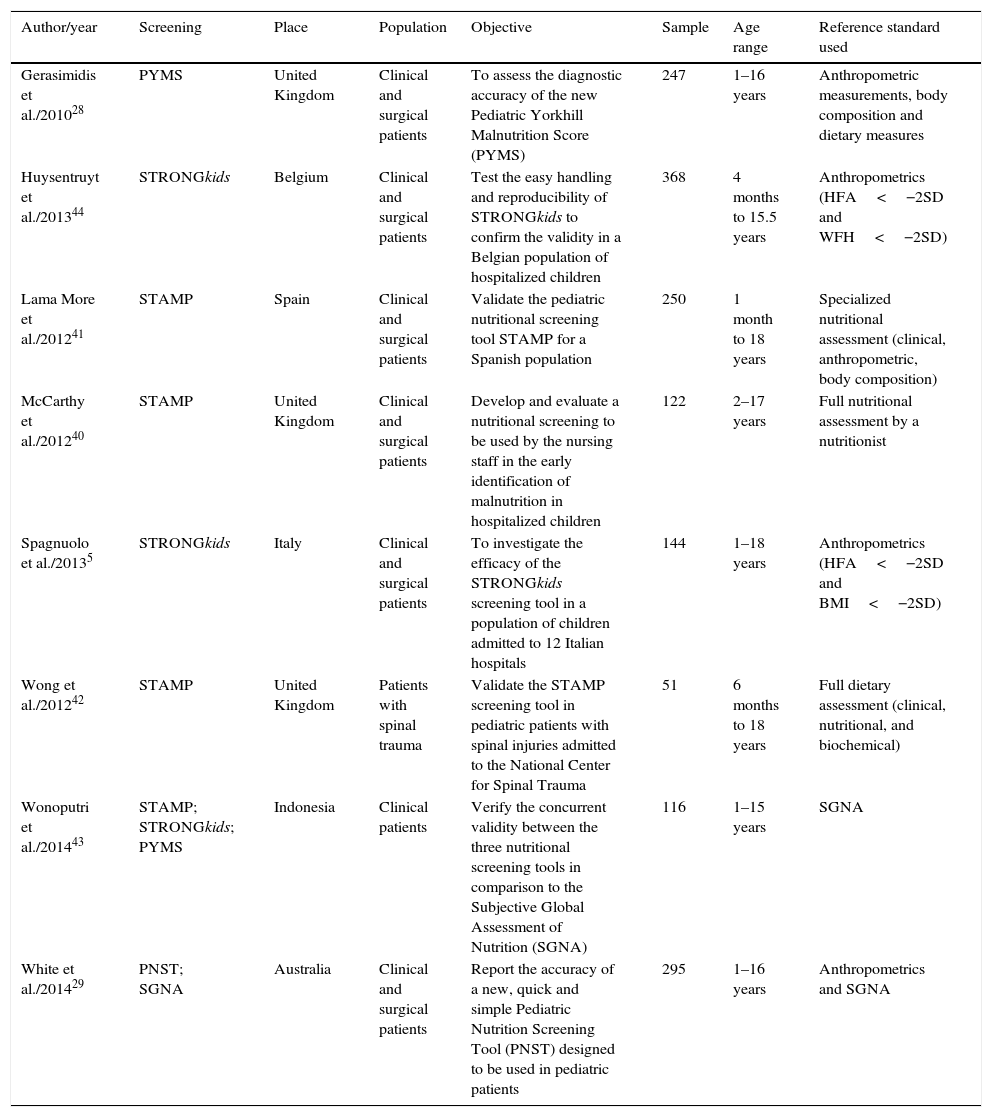
Of the eight selected studies, three (37.5%) were published in 2012. The age of the individuals who participated in the studies ranged from 1 month to 18 years. A complete description of the articles is shown in Table 1.
Characterization of the articles included in the systematic review.
| Author/year | Screening | Place | Population | Objective | Sample | Age range | Reference standard used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gerasimidis et al./201028 | PYMS | United Kingdom | Clinical and surgical patients | To assess the diagnostic accuracy of the new Pediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score (PYMS) | 247 | 1–16 years | Anthropometric measurements, body composition and dietary measures |
| Huysentruyt et al./201344 | STRONGkids | Belgium | Clinical and surgical patients | Test the easy handling and reproducibility of STRONGkids to confirm the validity in a Belgian population of hospitalized children | 368 | 4 months to 15.5 years | Anthropometrics (HFA<−2SD and WFH<−2SD) |
| Lama More et al./201241 | STAMP | Spain | Clinical and surgical patients | Validate the pediatric nutritional screening tool STAMP for a Spanish population | 250 | 1 month to 18 years | Specialized nutritional assessment (clinical, anthropometric, body composition) |
| McCarthy et al./201240 | STAMP | United Kingdom | Clinical and surgical patients | Develop and evaluate a nutritional screening to be used by the nursing staff in the early identification of malnutrition in hospitalized children | 122 | 2–17 years | Full nutritional assessment by a nutritionist |
| Spagnuolo et al./20135 | STRONGkids | Italy | Clinical and surgical patients | To investigate the efficacy of the STRONGkids screening tool in a population of children admitted to 12 Italian hospitals | 144 | 1–18 years | Anthropometrics (HFA<−2SD and BMI<−2SD) |
| Wong et al./201242 | STAMP | United Kingdom | Patients with spinal trauma | Validate the STAMP screening tool in pediatric patients with spinal injuries admitted to the National Center for Spinal Trauma | 51 | 6 months to 18 years | Full dietary assessment (clinical, nutritional, and biochemical) |
| Wonoputri et al./201443 | STAMP; STRONGkids; PYMS | Indonesia | Clinical patients | Verify the concurrent validity between the three nutritional screening tools in comparison to the Subjective Global Assessment of Nutrition (SGNA) | 116 | 1–15 years | SGNA |
| White et al./201429 | PNST; SGNA | Australia | Clinical and surgical patients | Report the accuracy of a new, quick and simple Pediatric Nutrition Screening Tool (PNST) designed to be used in pediatric patients | 295 | 1–16 years | Anthropometrics and SGNA |
PYMS, Pediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score; STRONGkids, Screening Tool Risk on Nutritional Status and Growth; STAMP, Screening Tool for the Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics; PNST, Pediatric Nutrition Screening Tool; SGNA, Subjective Global Nutritional Assessment; HFA, height for age; WFH, weight for height; BMI, body mass index for age; SD, standard deviation.
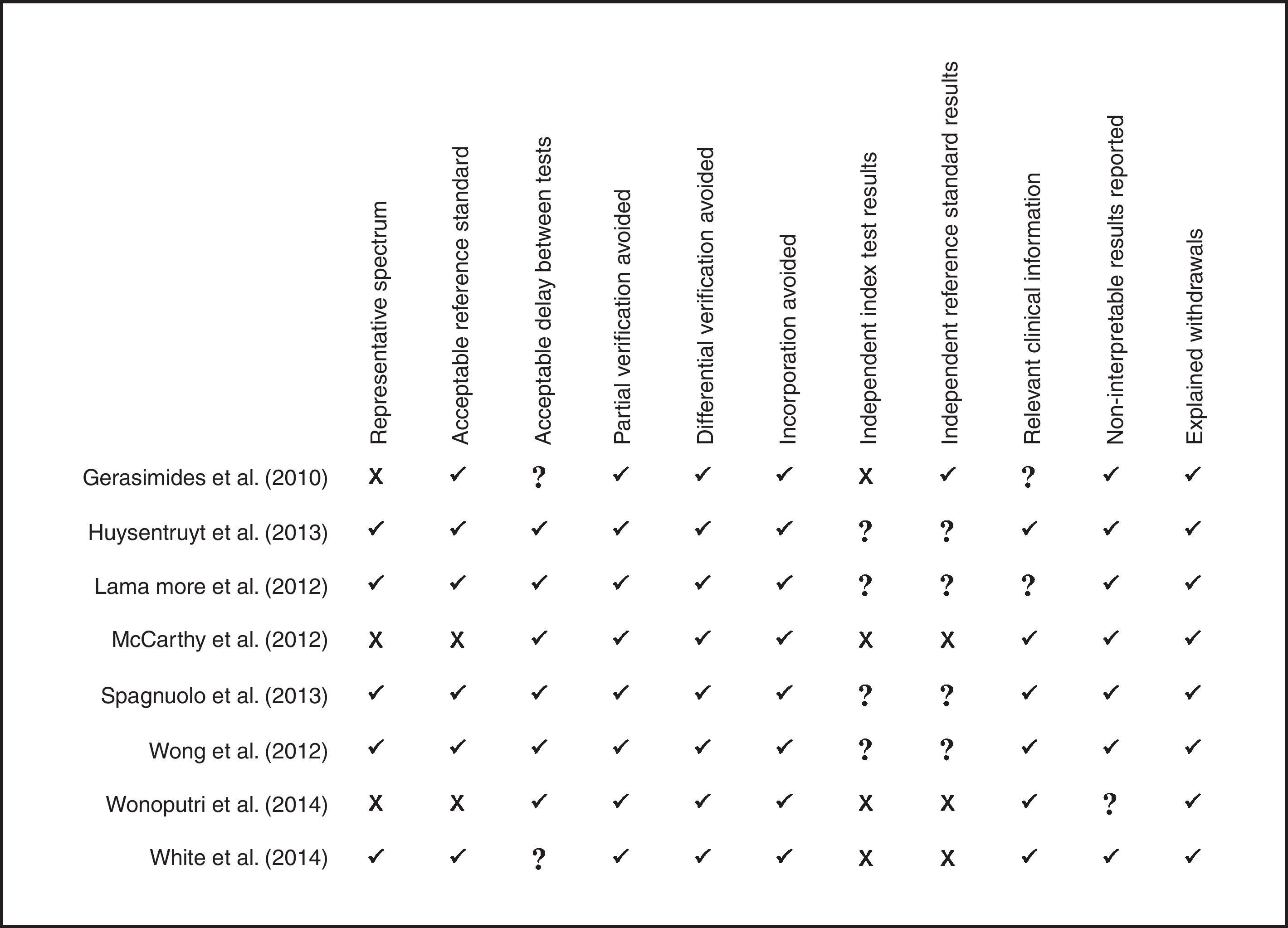
The assessment of the methodological quality of the articles showed that most (62.5%, n=5) had “good methodological performance”. In three of the articles (37.5%), the sample was not representative of the population. The authors observed heterogeneity in the choice of the reference standard. In this respect, two studies (25%) did not have an adequate reference standard (anthropometry), and furthermore, the information of four studies (50%) did not allow to verify whether the interpretation of results of the reference test and the index test was independently performed in the included studies, or if there was review bias. The result of the methodological quality assessment, according to the modified version of QUADAS,36 is shown in Fig. 2.
The analysis of the studies showed the use of five nutritional risk screening tools in hospitalized pediatric patients: Screening Tool for the Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics (STAMP)40–43 in four (50%) of the studies, Screening Tool Risk on Nutritional Status and Growth (STRONGkids)5,43,44 in three (37.5%), Pediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score (PYMS)28,43 in two (25%), Pediatric Nutrition Screening Tool (PNST)29 in one (12.5%), and the Subjective Global Nutritional Assessment (SGNA)29 in one (12.5%).
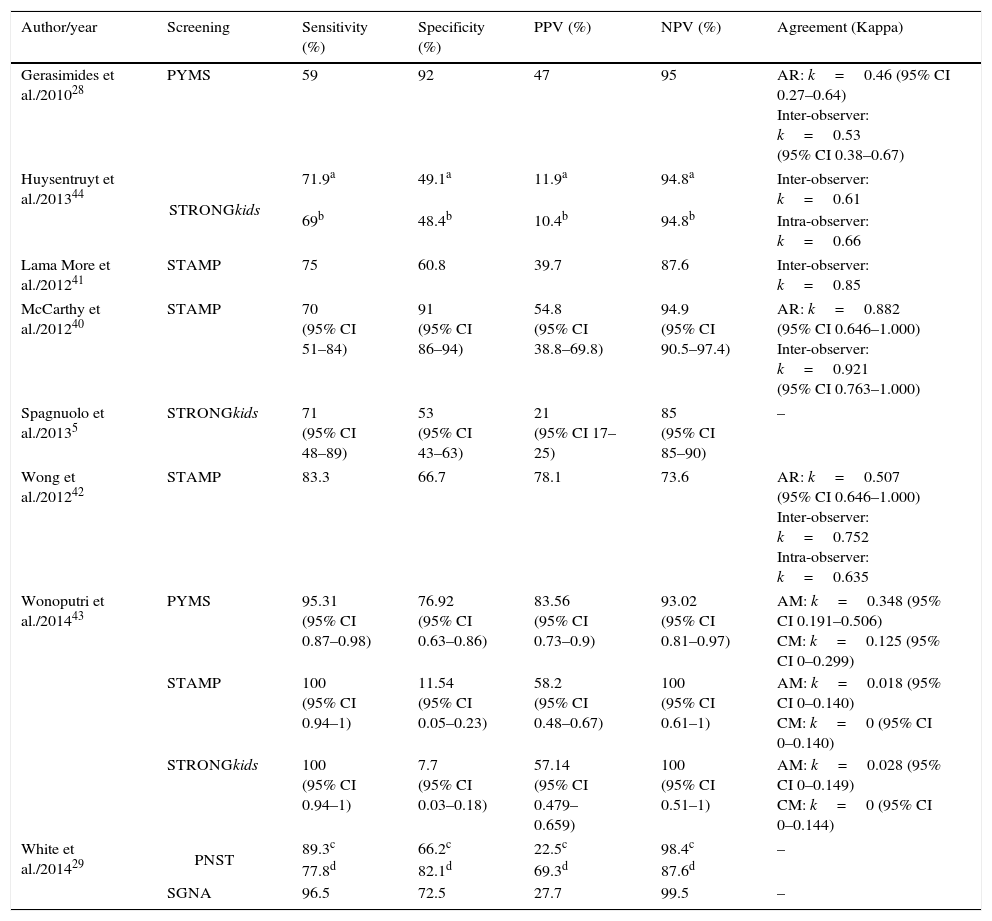
The sensitivity of the screening tools ranged from 59%28 to 100%.43 STAMP and STRONGkids showed the best results regarding sensitivity (100%).
Most tools had a specificity between 53%5 and 92%;28 for this parameter, STRONGkids and STAMP had the lowest percentages of specificity, 7.7%43 and 11.54%,43 respectively, whereas PYMS had high specificity (92%).28 It was also observed that all studies had high negative predictive value (between 73.6% and 100%).
The agreement between nutritional risk screening and the reference standard was verified in four of the studies (50%), with better performance of STAMP40 (k=0.882, 95% CI: 0.646–1.000). Regarding the interobserver agreement, it varied from moderate (0.40–0.59)28 to almost perfect (0.80–1.00);40,41 the STAMP tool showed the best interobserver agreement. For the intraobserver agreement, STRONGkids44 showed the best performance, with substantial agreement (k≥0.60–.79; Table 2).
Sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, and reproducibility of the studies included in the systematic review.
| Author/year | Screening | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | Agreement (Kappa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gerasimides et al./201028 | PYMS | 59 | 92 | 47 | 95 | AR: k=0.46 (95% CI 0.27–0.64) Inter-observer: k=0.53 (95% CI 0.38–0.67) |
| Huysentruyt et al./201344 | STRONGkids | 71.9a | 49.1a | 11.9a | 94.8a | Inter-observer: k=0.61 |
| 69b | 48.4b | 10.4b | 94.8b | Intra-observer: k=0.66 | ||
| Lama More et al./201241 | STAMP | 75 | 60.8 | 39.7 | 87.6 | Inter-observer: k=0.85 |
| McCarthy et al./201240 | STAMP | 70 (95% CI 51–84) | 91 (95% CI 86–94) | 54.8 (95% CI 38.8–69.8) | 94.9 (95% CI 90.5–97.4) | AR: k=0.882 (95% CI 0.646–1.000) Inter-observer: k=0.921 (95% CI 0.763–1.000) |
| Spagnuolo et al./20135 | STRONGkids | 71 (95% CI 48–89) | 53 (95% CI 43–63) | 21 (95% CI 17–25) | 85 (95% CI 85–90) | – |
| Wong et al./201242 | STAMP | 83.3 | 66.7 | 78.1 | 73.6 | AR: k=0.507 (95% CI 0.646–1.000) Inter-observer: k=0.752 Intra-observer: k=0.635 |
| Wonoputri et al./201443 | PYMS | 95.31 (95% CI 0.87–0.98) | 76.92 (95% CI 0.63–0.86) | 83.56 (95% CI 0.73–0.9) | 93.02 (95% CI 0.81–0.97) | AM: k=0.348 (95% CI 0.191–0.506) CM: k=0.125 (95% CI 0–0.299) |
| STAMP | 100 (95% CI 0.94–1) | 11.54 (95% CI 0.05–0.23) | 58.2 (95% CI 0.48–0.67) | 100 (95% CI 0.61–1) | AM: k=0.018 (95% CI 0–0.140) CM: k=0 (95% CI 0–0.140) | |
| STRONGkids | 100 (95% CI 0.94–1) | 7.7 (95% CI 0.03–0.18) | 57.14 (95% CI 0.479–0.659) | 100 (95% CI 0.51–1) | AM: k=0.028 (95% CI 0–0.149) CM: k=0 (95% CI 0–0.144) | |
| White et al./201429 | PNST | 89.3c | 66.2c | 22.5c | 98.4c | – |
| 77.8d | 82.1d | 69.3d | 87.6d | |||
| SGNA | 96.5 | 72.5 | 27.7 | 99.5 | – | |
PYMS, Pediatric Yorkhill Malnutrition Score; STRONGkids, Screening Tool Risk on Nutritional Status and Growth; STAMP, Screening Tool for the Assessment of Malnutrition in Pediatrics; PNST, Pediatric Nutrition Screening Tool; SGNA, Subjective Global Nutritional Assessment; PPV, positive predictive value; NPV, negative predictive value; AR, agreement with the reference standard used; AM, acute malnutrition; CM, chronic malnutrition; CI, confidence interval; HFA, height for age; WFH, weight for height; BMI, body mass index for age.
A systematic review is a valuable tool, both in individual diagnostic test assessment and to compare different tests in a same target-condition. Its results may dispel clinical doubts or explore other questions, showing the way so that the answer can be found in the best way.45
This systematic review of diagnostic accuracy studies synthesized the results of several studies that evaluated nutritional risk screening tools to be used in hospitalized pediatric patients.
The methodological quality of most studies was considered high. The main methodological problems were related to lack of adequate information to determine whether the interpretation of the nutritional screening used was independent or whether there was influence of the knowledge of the reference standard results, or vice versa, characterizing a review bias of the results.
In this aspect, the review bias can lead to inflated measures of diagnostic accuracy, and also, depending on the degree of subjectivity associated to the index test (screening), its interpretation can be strongly influenced when the standard reference result is known.36
In 37.5% of the studies, the sample was not representative, contrary to what recommends the Cochrane Handbook for diagnostic accuracy studies,37 which recommends that an appropriate sample should be defined, configuring one of the main factors that can affect the test accuracy.
Regarding the reference standard used, this is still a controversial point, given the lack of a universally accepted gold standard for the diagnosis of nutritional risk in children.43
Among the studies, it was observed that some used the assessment performed by a nutritionist as a reference standard. This parameter is considered inappropriate by other authors, who point out that not all countries have nutrition professionals, and their role can vary depending on the country.32,43,46 In this matter, anthropometrics has been better assessed as a reference standard, since it uses universally accepted parameters44 and is recommended by an international reference organization.47
The nutritional screening tool must be able to identify those patients that may benefit from the intervention, because they are either at risk of having or developing complications that are avoidable through adequate nutritional support.41
Screening methods consist in the systematization of questions that investigate the existence of characteristics that may reflect or be related to nutritional deterioration.15 In this regard, nutritional screening detects only the presence of malnutrition risk. Conversely, nutritional assessment, not only detects malnutrition, but also classifies its degree and allows for the collection of information to assist in its correction.48
The STAMP tool was validated in a study performed in the United Kingdom.49 This nutritional screening tool considers three elements: the patient's clinical diagnosis and its nutritional implications (if any), the child's nutritional intake during hospitalization, and anthropometric measurements (where the measured value of the child's height and weight is recorded and compared to reference values by age and gender).10
The PYMS was developed and validated by Gerasimides et al.28 in the United Kingdom. It evaluates four predictors or recognized symptoms of malnutrition risk: body mass index (BMI), recent weight loss history, changes in food intake, and the expected effect of the current medical condition on the patient's nutritional status.28
The STRONGkids, proposed by Hulst et al. in a multicenter study in the Netherlands,1 is a questionnaire comprising four areas: global subjective assessment; nutritional risk of the patient's disease (presence of high-risk disease or predicted major surgery); nutritional intake and losses (decreased food intake, diarrhea and vomiting), and loss or absence of weight gain.1,30,50,51 This is the only tool translated and culturally adapted into Portuguese.30
The PNST was designed by White et al.29 in Australia. It consists of four simple yes/no questions related to involuntary weight loss in recent days, poor weight gain in recent months, decrease in food intake in recent weeks and, also, if the child is thin or obese.32 Nutritional risk is considered when there are two positive answers to the questions.29,32
The SGNA is an adaptation of the Subjective Global Assessment, which has been validated for use in pediatric patients.52 It consists of a questionnaire that collects and analyze several data: adequacy of the current height for age; adequacy of current weight for height; unintentional weight alterations; food intake; gastrointestinal symptoms; metabolic stress from the disease; and physical examination. Although mentioned as a screening tool, it is better characterized as a structured nutritional assessment.4
Based on the components evaluated in the screening tools (STAMP, STRONGkids, and PYMS), a score was obtained that corresponds to the malnutrition risk level, described as low, moderate, or high, differently from the SGNA, which classifies patients as well nourished, moderately malnourished, and severely malnourished.
With the exception of SGNA, which was developed for use in adult patients and subsequently validated for use in pediatric patients,52 all evaluated screening tools were developed for the pediatric population.
The evaluations of diagnostic accuracy in individual studies focus on the analysis of the index test performance compared to a reference test (sensitivity and specificity) or on the implications of positive and negative results of the index test.38 In this context, Hartman et al.4 point out that the sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility characteristics are essential for any tool aimed at nutritional assessment in pediatrics.
The STRONGkids and STAMP tools showed higher sensitivity and very low levels of specificity. Conversely, the PYMS showed better percentage of specificity. This finding may be related to the reference standard used in the studies, considering that, among the studies that had anthropometrics as the reference standard, no significant differences were found regarding these measurements, thus confirming the importance of an appropriate reference standard selection, since this choice can have important clinical implications.47
In the case of nutritional risk assessment in children, higher sensitivity and positive predictive value reflect an increased likelihood that the child who was identified at nutritional risk by the tool is actually in this situation.40
The tools that have low sensitivity are more susceptible to false-negative results; therefore, children who really are at nutritional risk are not diagnosed. As for those that have low specificity, they are more likely to provide false-positive results, implying in a diagnosis of risk in patients that do not have it.
The screenings should have high sensitivity in order to minimize the number of false negatives.34 In this context, sensitivity is more important than specificity, because a false-positive result will only expose the patient to a detailed nutritional assessment, whereas a false negative can result in an undetected malnourishment condition.44
The higher the degree of sensitivity of a test, the better its negative predictive value is, and thus, the greater the certainty that the individual with a negative result actually does not have the disease. And the more specific a test is, the better its positive predictive value (that is, the greater the confidence that a person with a positive result has the disease being assessed).34
Regarding the analysis of reproducibility and reliability, key measures to evaluate the accuracy of a nutritional screening tool, better performance of the STAMP and STRONGkids tools was observed (inter and intraobserver agreement, respectively). For the screening tool to have a reproducible measurement, it must have a good agreement, to reflect a high level of reliability.42
Regarding the applicability in pediatric practice, the ideal screening tool is the one that can quickly and reliably evaluate the patient's nutritional risk in order to indicate those who need a more detailed assessment and intervention.32,46 If the screening tool is extensive, it is less likely to be used by health care providers.1
The studies by Spagnuolo et al.5 and Huysentruyt et al.44 presented the STRONGkids as a simple structure tool, of practical use in routine care (mean of three minutes) and easily applied in a hospital. A study that methodologically analyzed six pediatric nutritional screening tools also pointed out the STRONGkids as the easiest, most practical, and most reliable test.46
A study with pediatric patients from New Zealand, comparing the PYMS, the STAMP and the STRONGkids screening tests, showed that the all three are viable and able to identify nutritional risk, but the STRONGkids was the most reliable in that population.53 In contrast, when comparing these same tools applied to hospitalized children in Indonesia, Wonoputri et al.43 recommend the PYMS as the most reliable in that setting.
The STAMP is described as a more detailed instrument, with longer application time (±10min), possibly due to the interpretation of growth charts.10 In this regard, the SGNA is reported as an extensive and time-consuming tool.43 The STRONGkids has been considered faster to apply due to the exclusion of weight and height;11 however, some authors5,43 regards the exclusion of an objective evaluation as a disadvantage of this tool.
The studies included in this review showed that most nutritional screening tools in pediatric patients are viable for nutritional risk screening in pediatrics. However, all the tools presented advantages and limitations, which is in agreement with several studies that reinforce the need for more research in the area.28,40,54–56 Moreover, only one of these tools has been translated and adapted into Portuguese language, which is a gap in the scientific production in this area.
Internationally, there are several recommendations regarding the performance of nutritional screening; however, they focus on adults and the elderly, due to the lack of an appropriate tool to identify nutritional risk in children on hospital admission.40 In this sense, Sykorová and Zavřelová10 emphasize the need for pediatric screening tools that are not only implemented, but truly functional, being targets of international accreditation standards and indicators of quality of care.
Furthermore, nutritional risk screening should be followed by regular assessments at the monitoring during hospitalization.46 In this respect, STRONGkids, STAMP, and PYMS were originally designed for regular use in patients with prolonged hospital stay. However, their applicability for this objective requires further investigations.
Regarding the limitations of this systematic review, although the search process was extensive and detailed, there is a probability that important information has been lost due to articles published in other languages rather than English, Spanish, and Portuguese.
ConclusionNutritional risk screening is essential for the care of hospitalized pediatric patients. As for the choice of the screening tool to be used in hospital practice, it is imperative to know the aspects related to their clinical performance and diagnostic accuracy.
The studies included in this systematic review showed good clinical performance of the malnutrition risk screening tools in pediatric patients, mainly the STRONGkids and STAMP tools.
However, more research is necessary in order to explore the several aspects of the clinical application of these tools. Brazilian studies on this subject are incipient. Only the STRONGkids tool has been translated and adapted for the population of hospitalized Brazilian children, and therefore, it is critical for future studies to adapt and validate the other tools, considering their clinical performance and diagnostic accuracy for this population.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Teixeira AF, Viana KD. Nutritional screening in hospitalized pediatric patients: a systematic review. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2016;92:343–52.
Study associated with the Multidisciplinary Residency Program in Health, Hospital Universitário, Universidade Federal do Maranhão (UFMA), São Luís, MA, Brazil.