We would like to thank Proaño et al., for their review and comments on our article “Variables associated with extra uterine growth restriction in very low birth weight infants”,1 which certainly contributed to a better understanding of our results.
We used Fenton 20032 as reference for data analysis in our previous article,1 since it was the reference available at the time. Encouraged by the letter from Proaño et al., we chose to recalculate using the New Fenton 2013 reference3 and did the analysis again. Indeed, different results were observed with this new reference.3
MethodsUsing the same data from the previous study,1 we used the Bulk Research Calculator, available at http://www.ucalgary.ca/fenton/2013chart, to calculate the Z-scores for weight and head circumference (HC), and observed the following results:
New resultsOf the population studied, 49% were males, 67.4% of the newborns were appropriate for gestational age (AGA), and 32.6% were small for gestational age (SGA). It was observed that although the mean Z-score for HC decreased slightly during the hospitalization period (-0.495 to -0.496), the mean weight Z-score showed worsening (-0.958 to -1.798). Of the 570 newborns evaluated, 39.1% presented growth restriction at discharge, considering weight, and 7.5% when the evaluated variable was HC.
AGA infants presented a reduction in weight Z-score (-0.52 to -1.46) and HC Z-score (-0.03 to -0.29). In SGA infants, the decrease in weight Z-score was lower (-1.87 to -2.49) when compared to AGA infants, and the HC Z-score showed an increase (-1.46 to -0.93). Of the 32.6% (186/570) infants born SGA, 73.7% (137/186) had extra uterine growth restriction (EUGR) at discharge considering weight and 12.9% (24/186) considering HC. Rates of EUGR for AGA infants were 22.4% (86/384) considering weight and 4.9% (19/384) considering HC. These differences were statistically significant for weight (p = 0.000) and HC (p = 0.001). Regarding growth restriction, it was observed that, at birth, 11.4% of the newborns studied had intra uterine growth restriction (IUGR), considering weight. Upon discharge, this rate of growth restriction had increased to 39.1%. Regarding HC, the rate of growth restriction at birth was 9.5% and at discharge, 7.5%.
At the univariate analysis, the variables that presented statistical significance when the outcome variable was the HC Z-score at discharge were: SGA (PR = 1.08; 95% CI: 1.03-1.14), oxygen use at 36 weeks (PR = 1.14; 95% CI: 1.04-1.24), patent ductus arteriosus (PDA; PR = 1.06; 95% CI: 1.01-1.11), and hospital length of stay (PR =1.01; 95% CI: 1.01-1.02). For the weight Z-score at hospital discharge these variables were: maternal hypertension (PR = 1.26; 95% CI: 1.02-1.54), oxygen use at 36 weeks (PR = 1.48; 95% CI: 1.18-1.87), SGA (PR = 3.29; 95% CI: 2.68-4.04), respiratory distress syndrome (RDS; PR= 0.79; 95% CI: 0.64-0.97), and hospital length of stay (PR = 1.01; 95% CI: 1.01-1.02). Proven sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) presented low frequency in the population, 4.6% and 1.2%, respectively, and were not included in the regression analysis.
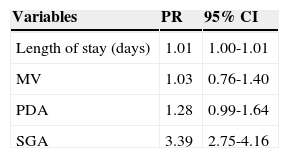
At the regression analysis, using as outcome the HC Z-score ≤ -2 corrected for gestational age at discharge, the variables that entered in the final model had statistical significance: hospital length of stay and be SGA at birth (Table 1).
Variables in the final model of Poisson regression for HC Z-score at hospital discharge.
| Variables | PR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Length of stay (days) | 1.01 | 1.00-1.01 |
| MV | 1.03 | 0.76-1.40 |
| PDA | 1.28 | 0.99-1.64 |
| SGA | 3.39 | 2.75-4.16 |
HC, head circumference; CI, confidence interval; PR, prevalence ratio; MV; mechanical ventilation; PDA, patent ductus arteriosus; SGA, small for gestational age.
Variables included in the analysis: gender, SGA, use of antenatal steroids, maternal hypertension, PDA, respiratory distress syndrome, use of MV, oxygen use at 36 weeks, and length of stay.
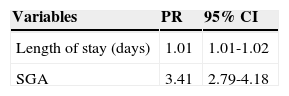
It was observed that adding one day in the length of stay increased by 1% the chance of growth restriction at discharge, and SGA birth increased this risk by three times. When the outcome was weight Z-score ≤ -2 for corrected age at discharge, the variables that remained in the final model were: length of hospital stay and SGA birth (Table 2). Adding one day to the hospital length of stay resulted in a 1% increase in the chance of having growth restriction at discharge. The risk factor with the greatest impact was SGA.
Variables of the final model of Poisson regression for weight Z-score at hospital discharge.
| Variables | PR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Length of stay (days) | 1.01 | 1.01-1.02 |
| SGA | 3.41 | 2.79-4.18 |
PR, prevalence ratio; CI, confidence interval; SGA, small for gestational age.
Variables included in the analysis: gender, SGA, use of antenatal steroids, maternal hypertension, patent ductus arteriosus, respiratory distress syndrome, mechanical ventilation, oxygen use at 36 weeks, and length of stay.
In conclusion, when we re-analyzed the data, the results were worse than with the previously used reference, and the most important factors associated with a extra-uterine growth restriction were being SGA and length of stay, which probably reflects disease severity.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Lima PA, de Carvalho M, da Costa AC, Moreira ME. Author's reply: Z-Score: Fenton 2013. Ten-year update. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2014;90:427–428.